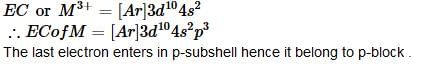Chemical Bonding - Main Group - Periodic Properties - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Bonding - Main Group - Periodic Properties
The inter-nuclear distance in O—O bonds for 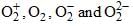 respectively are:
respectively are:
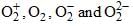 respectively are:
respectively are: Arrange the following compounds in their C—H bond length:
(I) CH3F (II) CH2F2 (III) CHF3
(I) CH3F (II) CH2F2 (III) CHF3
Arrange the following species in increasing order of stability:
Li2, Li2+, Li2–
Li2, Li2+, Li2–
Which of the following is correct structure of S2Cl2?
Elements X and Y have valence shell electronic configuration as:
X: ns2np5 , Y: ns2np3
Which compound is likely to be formed?
M+3 has electronic configuration as [Ar]3d104s2, hence it lies in following block:
Pick out the property which is not shown by transition metals:
When is the Intramolecular hydrogen bond formed?
Which among the following is both a molecule and a compound?
Standard reduction potentials in acidic medium for F2, Cl2, Na, Zn are in the order:
Consider the compounds PF5, SbF5, PH3 and SbH3. The strongest acid and strongest base among these are resp:
Among SiCl4, P(O)Cl3, NF3, trans-[SnCl4(py)2] (py = pyridine), those with zero dipole moments are:
The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in:
Ionic hydrides reacts with water to give
Consider (I) I-, (II) Se2-, (III) Br‑, (IV) O2-, (V) F- and arrange them in decreasing order of ionic radius.
Which pair is different from others?
The d-bond is formed via the overlap of (considering z-axis as the inter-nuclear axis):
First, Second and Third ionization energy values are 100 eV, 150 eV and 1500 eV. Element can be?
Which of the following compunds is not formed by all alkali metals?
What are the hydrolysis products of calcium carbide?
Noble gases (like He, Ne, Ar, Kr etc) are isolated from air. One of the steps is/are
To an acidified dichromate solution, a pinch of Na2O2 and ether is added and shaken. What is the observation?
The reason for the chemical inertness of gaseous nitrogen at room temperature is best given by its:
The correct increasing order of melting points of the following is:
Which reaction lead to adduct formation:
Which represents Alkali metals based on IE1and IE2 values?
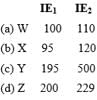
Which is best oxidizing agent?