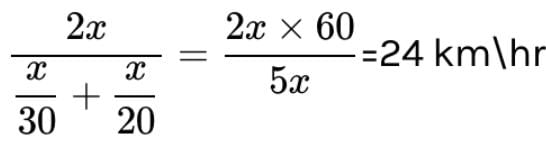Test: Motion in a Straight Line - 2 - Grade 11 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Motion in a Straight Line - 2
A particle covers half of the circle of radius r. Then the displacement and distance of the particle are respectively -
A hall has the dimensions 10m × 10m × 10 m. A fly starting at one corner ends up at a diagonally opposite corner. The magnitude of its displacement is nearly
A car travels from A to B at a speed of 20 km h-1 and returns at a speed of 30 km h-1. The average speed of the car for the whole journey is
A car travels a distance of 2000 m. If the first half distance is covered at 40 km/hour and the second half at velocity v and if the average velocity is 48 km/hour, then the value of v is -
At an instant t , the co-ordinates of a particle are x = at2, y = bt2 and z = 0 , then its velocity at the instant t will be
A car runs at constant speed on a circular track of radius 100 m taking 62.8 s on each lap. What is the average speed and average velocity on each complete lap?
The displacement of a body is given by 2s = gt2 where g is a constant. The velocity of the body at any time t is
A particle is moving so that its displacement s is given as s = t3- 6t2 + 3t + 4 meter. Its velocity at the instant when its acceleration is zero will be-
A body starts from rest and is uniformly accelerated for 30 s. The distance travelled in the first 10s is x1, next 10 s is x2 and the last 10 s is x3. Then x1 : x2 : x3 is the same as
The displacement-time graph of a moving particle is shown below. The instantaneous velocity of the particle is negative at the point
The variation of velocity of a particle moving along straight line is shown in the figure. The distance travelled by the particle in 4 s is
The displacement time graphs of two particles A and B are straight lines making angles of respectively 30º and 60º with the time axis. If the velocity of A is vA and that of B is vB then the value of is
The v-t graph of a linear motion is shown in adjoining figure. The distance from origin after 8 seconds is
The adjoining curve represents the velocity-time graph of a particle, its acceleration values along OA, AB and BC in metre/sec2 are respectively-
In the following velocity-time graph of a body, the distance and displacement travelled by the body in 5 second in meters will be -
If position time graph of a particle is sine curve as shown, what will be its velocity-time graph
A particle, after starting from rest , experiences, constant acceleration for 20 seconds. If it covers a distance of S1, in first 10 seconds and distance S2 in next 10 sec, then
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4sec to reach the bottom after starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one fourth the distance starting from the top
The initial velocity of a particle is 10 m/sec and its retardation is 2 m/sec2. The distance covered in the fifth second of the motion will be
A body starts from rest, the ratio of distances travelled by the body during 3rd and 4thseconds is :
A body is dropped from a height h under acceleration due to gravity g. If t1 and t2 are time intervals for its fall for first half and the second half distance, the relation between them is
Two bodies of different masses ma and mb are dropped from two different heights, viz a and b. The ratio of times taken by the two to drop through these distances is
A body is thrown upward and reaches its maximum height. At that position-
Two trains each of length 50 m are approaching each other on parallel rails. Their velocities are 10 m/sec and 15 m/sec. They will cross each other in -
A car A is going north-east at 80 km/hr and another car B is going south-east at 60 km/hr. Then the direction of the velocity of A relative to B makes with the north an angle a such that tan a is -
An object A is moving with 10 m/s and B is moving with 5 m/s in the same direction of positive x-axis. A is 100 m behind B as shown. Find time taken by A to Meet B
A ball is thrown upwards. It returns to ground describing a parabolic path. Which of the following remains constant ?
The angle of projection of a body is 15º . The other angle for which the range is the same as the first one is equal to-
A ball is thrown at an angle of 45º with the horizontal with kinetic energy E. The kinetic energy at the highest point during the flight is-
The maximum range of a projectile is 22 m. When it is thrown at an angle of 15º with the horizontal, its range will be-