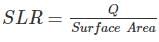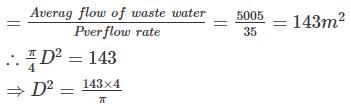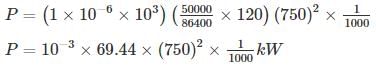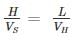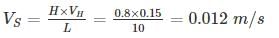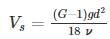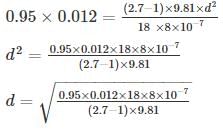Test: Environmental Engineering- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Engineering- 2
The effective size of the particle (D10) of filter [slow sand filter] is
The efficiency of sediment removal in a continuous flow sedimentation tank does not depend upon-
The design parameter for flocculation is given by a dimensionless number Gt, where G is the velocity gradient and t is the detention time. Values of Gt ranging from 104 to 105 are commonly used, with t ranging from 10 to 30 min. the most preferred combination of G and t to produce smaller and denser flocs is
A circular primary clarifier processes an average flow of 5005 m3/d of municipal wastewater. The overflow rate is 35 m3/m2/d. the diameter of clarifier shall be
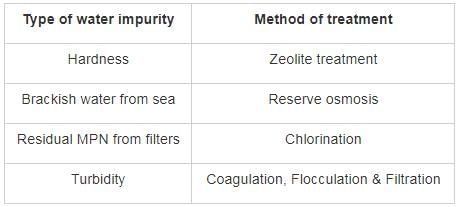
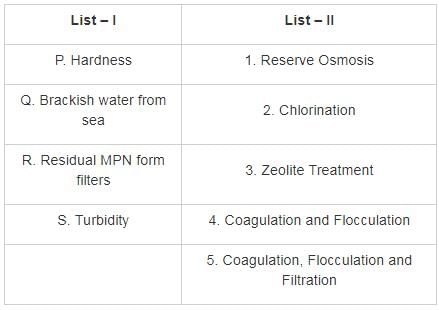
Match List – I (Type of water impurity) with List – II (Method of treatment) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
For water, the dosage at a breakpoint is 1.5 mg/L and residual chlorine at that time is found to be 0.3 mg/L. If cumulative chlorine added is 2 mg/L, the total residual chlorine will be –
A water treatment plant is required to process 50,000 m3 water per day. The rapid mixing tank will blend 50 mg/L of alum with the flow and have a detention time of 2 min. The power input (in kilowatt) necessary for a G value of 750 S-1 at water temperature 22°C is _____.
(use kinematic viscosity at 22°C as 1 × 10-6 m2/s)
A channel-type grit chamber has a flow-through velocity of 0.15 m/s, a depth of 0.8 m and a length of 10 m. For inorganic particles with the specific gravity of 2.7, and considering kinematic viscosity of 8×10-7 m2/s the largest diameter that can be removed with 95% efficiency is