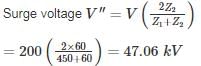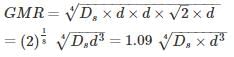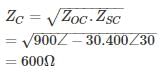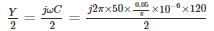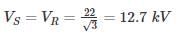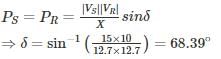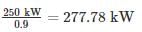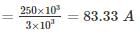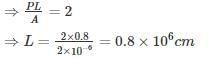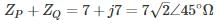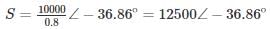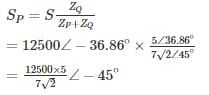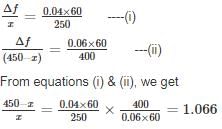Test: Power Systems- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Power Systems- 2
When series reactor is used in generating stations, the fault current magnitude is
A surge of 200 kV travels along an overhead line towards its junction with a cable. The surge impedance for the overhead line and cable are 450 Ω and 60 Ω respectively. The magnitude of the surge transmitted through cable is – (in kV)
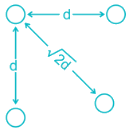
Ds is the GMR of each sub-conductor of a four sub-conductor bundle conductor and dd is the bundle spacing. What is the GMR of the equivalent single conductor?
A transmission line having open circuit impedance and short circuit impedance parameters are respectively Zoc = 900∠ − 30∘, ZSC = 400∠30∘ , Find the characteristic impedance of the line – (in Ω)
A three-phase, 50 Hz transmission line of length 120 km has a capacitance of 0.05/π μF/km It is represented as a π – model. The shunt admittance at each end of the transmission line will be
A three-phase, 22 kV line feeds a per – phase load of 15 MW. If the impedance of the Line is Z = j 10Ω, then the value of load angle to maintain a line voltage of 22 kV at the load is_____ (in degrees)
What is the maximum length (in km) for a single phase transmission line having a copper conductor of 0.8 cm2 cross-section over which 250 kW at unity power factor and at 3 kV are to be delivered?
The efficiency of transmission is 90%. The specific resistance as 2 μΩ-cm.
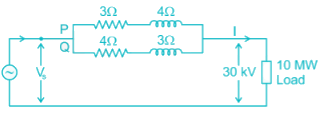
Two overhead Lines ‘P’ and ‘Q’ are connected in parallel to supply a load of 10 MW at 0.8 pf lagging. The resistance and reactance of line ‘P’ are 3 Ω and 4 Ω, respectively and of the Line, ‘Q’ is 4 Ω and 3 Ω respectively. The power supplied by the ‘P’ is
The load on an installation is 600 kW, 0.8 lagging p.f. which works for 3000 hours per annum. The tariff is Rs. 100 per KVA plus 20 Paise per kWh. If the power factor is improved to 0.9 lagging by means of loss of free capacitors costing Rs. 60 per kVAR, calculate the annual cost saving (in Rupees). Allow 10% per annum for interest and depreciation on capacitors.
Two generators rated 250 MW and 400 MW are operating in parallel. The droop characteristics of the governors are 4% and 6% respectively.if a load of 450 MW is share between them. What will be the system frequency? Assume nominal system frequency is 60 Hz and no governing action.