Chemical Kinetics MCQ - 1 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Kinetics MCQ - 1 (Advanced)
Ozone decomposes according to the equation
2O3(g) → 3O2(g) Mechanism of the reaction is
Step I : O3(g) 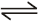 O2(g) + O(g) (fast)
O2(g) + O(g) (fast)
Step II : O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g) (slow)
Which of the following is correct ?
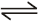 O2(g) + O(g) (fast)
O2(g) + O(g) (fast) Consider the following case of competing 1st order reactions After the start of the reaction at t = 0, with only P, concentration of Q is equal to R at all times. The time in which all the three 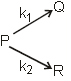
concentration will be equal is given by

A substance undergoes first order decomposition. The decomposition follows two parallel first order reactions as

The % distribution of B and C is ................ and .................. respectively.

The basic theory behind Arrhenious equation is that
Which of the following statements are correct about half life period ?
For a reaction : 2A + 2B → products, the rate law expression is r = k[A]2 [B]. Which of the following is/are correct?
Which of the following statements are correct ?
Rate constant k varies with temperature by equation log10k(min-1) = 5 – 2000/T. We can conclude
A reaction is catalysed by H+ ion. In presence of HA, rate constant is 2 × 10-3 min-1and in presence of HB rate constant is 1 × 10-3 min-1. HA and HB being strong acids, we may conclude that
The elements which are good catalysts and have the ability to change their oxidation number are
Statement-1 : The time of completion of reactions of type A → product (order <1) may be determined.
Statement-2 : Reactions with order ³ 1 are either too slow or too fast and hence the time of completion can not be determined.
Statement-1 : Temperature coefficient of an one step reaction may be negative.
Statement-2 : The rate of reaction having negative order with respect to a reactant decreases with the increase in concentration of the reactant.
Statement-1 : The overall rate of a reversible reaction may decrease with the increase in temperature.
Statement-2 : When the activation energy of forward reaction is less than that of backward reaction, then the increase in the rate of backward reaction is more than that of forward reaction on increasing the temperature.
Statement-1 : In a reversible endothermic reaction, Eact of forward reaction is higher than that of backward reaction
Statement-2 : The threshold energy of forward reaction is more than that of backward reaction
A hypothetical elementary reaction 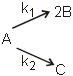 where
where 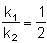 Initially only 2 moles of A are present.
Initially only 2 moles of A are present.
The total number of moles of A, B & C at the end of 50% reaction are
A hypothetical elementary reaction 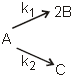 where
where 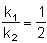 Initially only 2 moles of A are present.
Initially only 2 moles of A are present.
Number of moles of B are
The rate of a reaction increases significantly with increase in temperature. Generally, rates of reaction are doubled for every 10º rise in temperature. Temperature coefficient gives us an idea about the change in rate of a reaction for every 10º change in temperature.
Temperature coefficient 
Arrhenious gave an equation which describes rate constant k as a function of temperature is k = A –Ea/RT
where k is a rate constant
A is frequency factor or pre exponential factor
Ea is activation energy
T is temperature in kelvin and
R is universal gas constant
Equation when expressed in logarithmic form becomes
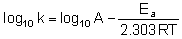
Q.
For a reaction Ea = 0 and k = 3.2 × 105 s-1 at 325 K. The value of k at 335 K would be
The rate of a reaction increases significantly with increase in temperature. Generally, rates of reaction are doubled for every 10º rise in temperature. Temperature coefficient gives us an idea about the change in rate of a reaction for every 10º change in temperature.
Temperature coefficient 
Arrhenious gave an equation which describes rate constant k as a function of temperature is k = A –Ea/RT
where k is a rate constant
A is frequency factor or pre exponential factor
Ea is activation energy
T is temperature in kelvin and
R is universal gas constant
Equation when expressed in logarithmic form becomes
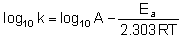
Q.
For which of the following reactions k310/k300 would be maximum ?
The rate of a reaction increases significantly with increase in temperature. Generally, rates of reaction are doubled for every 10º rise in temperature. Temperature coefficient gives us an idea about the change in rate of a reaction for every 10º change in temperature.
Temperature coefficient 
Arrhenious gave an equation which describes rate constant k as a function of temperature is k = A –Ea/RT
where k is a rate constant
A is frequency factor or pre exponential factor
Ea is activation energy
T is temperature in kelvin and
R is universal gas constant
Equation when expressed in logarithmic form becomes
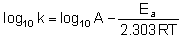
Q.
Activation energies of two reaction are Ea and Ea with Ea > Ea. If the temperature of the reacting systems is increased from T1 to T2 (k` are rate constants at higher temperature).
The rate of a reaction increases significantly with increase in temperature. Generally, rates of reaction are doubled for every 10º rise in temperature. Temperature coefficient gives us an idea about the change in rate of a reaction for every 10º change in temperature.
Temperature coefficient 
Arrhenious gave an equation which describes rate constant k as a function of temperature is k = A –Ea/RT
where k is a rate constant
A is frequency factor or pre exponential factor
Ea is activation energy
T is temperature in kelvin and
R is universal gas constant
Equation when expressed in logarithmic form becomes
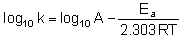
Q.
For the reactions, following data is given
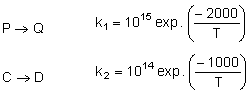
Temperature at which k1 = k2 is
The activation energy of a reaction at a given temperature is found to be 2.303 RT J mol–1. The ratio of rate constant to the Arrhenius factor is
An optically active compound A upon acid catalysed hydrolysis yield two optically active compound B and C by pseudo first order kinetics. The observed rotation of the mixture after 20 min was 5° while after completion of the reaction it was –20°. If optical rotation per mole of A, B & C are 60°, 40° & –80°. Calculate half life of the reaction.
Consider the following first order decomposition process:
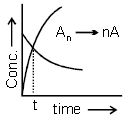
Here, "t" corresponds to the time at which (1/6)th of reactant is decomposed. The value of "n" is




















