Test: Our Body And Health - 2 - Class 5 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Our Body And Health - 2
The human body consists of different systems. These often work together to enable various processes to take place. Which two systems work together closely to make movement possible?
Blood is a vital body fluid that is transported throughout the body by the circulatory system. What are the functions of blood?
'X' is the living tissue in the human body that does not contain any blood vessel. Identify X.
Muscles are spread all over the human body. Their contraction and relaxation makes movements possible. Where is the strongest muscle that exerts most pressure in the human body present?
We need vitamin C for the growth and repair of tissues in all parts of the body, to make skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. Which of the following is the richest source of vitamin C?
This system, related to overall species survival, is responsible for allowing a species to produce young ones and to continue to allow their genes to get passed down. Which system are we talking about?
Ligaments are fibrous connective tissue that _______.
Which of the following disease is caused when plaque blocks the arteries which supply blood to the heart?
A human being's sense of balance helps prevent him from falling over when standing or moving. Many organs work together to achieve this, mainly the ear. Where in the ears is a human being's sense of balance located?
Bacteria are classified according to their shapes. The most common ones are cocci, which are spherical, and bacilli, which are rod-shaped. Which of the following is not a type of bacteria?
Sanitation facilities are vital for hygiene. These include proper waste disposal and the availability of toilets with running water. Which of the following diseases can be contracted due to lack of sanitation?
A child inherits characteristics from both its father and mother. What percentage of characteristics does it inherit from its mother?
Rama scraped her knee while climbing a tree at school. Which of the following systems responds to the wound by carrying white blood cells to it to help her fight infection?
These substances are special chemical messengers in the body that are created in the endocrine glands. They control most of the functions, from simple basic needs like hunger to complex systems like reproduction, and even the emotions and mood. What are these chemical messengers called?
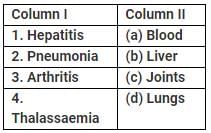
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.