Test: Quantitative Aptitude- 3 - GMAT MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Quantitative Aptitude- 3
Concentrated orange juice comes inside a cylinder tube with a radius of 2.5 inches and a height of 15 inches. The tubes are packed into wooden boxes, each with dimensions of 11 inches by 10 inches by 31 inches. How many tubes of concentrated orange juice, at the most, can fit into 3 wooden boxes?
A certain car’s price decreased by 2.5% (from the original price) each year from 1996 to 2002, during that time the owner of the car invested in a new carburetor and a new audio system for the car, which increased her price by $1,500. If the price of the car in 1996 was $22,000, what is the car’s price in 2002?
The average price of an antique car increases over the years. If from 1990 to 1996, the price of the car increased by 13% and from 1996 to 2001 it increased by 20%, what is the price of the car in 2001 if the price in 1990 was $11,500?
The apartment on King-Williams street is an asset that it’s value is tramping about.
From the year 1973 to 1983 it’s value decreased by 16% and from 1983 to 1993 it’s value increased by 16%. What is the value of the asset in 1993 if in 1973 it was worth $40,000?
The value of a “Tin-Rin” stock in the stock market decreased by 15% in the last two years.
The economic experts believe that the value of the stock will increase by 7% during the following year, which will make the value $440. What was the approximate price of the stock two years ago?
Which of the following expressions is equivalent to |X| <4 ?
Which of the following statements is equivalent to (8 + 2X < 18 – 6X < 23 + 2X)
At the faculty of Aerospace Engineering, 312 students study Random-processing methods, 232 students study Scramjet rocket engines and 112 students study them both. If every student in the faculty has to study one of the two subjects, how many students are there in the faculty of Aerospace Engineering?
In the faculty of Reverse-Engineering, 226 second year students study numeric methods, 423 second year students study automatic control of airborne vehicles and 134 second year students study them both. How many students are there in the faculty if the second year students are approximately 80% of the total?
In the Biotechnology class of 2000, there were X graduates. 32 of the graduates found a job, 45 continued on to their second degree and 13 did both. If only 9 people didn’t do both, What is X equal to?
In the equation (X + Y = k), k is a constant and X equals 13 when Y equals 23.5. What can be the value of X2 when Y2 is equal to 36?
Kramer can pack X boxes of cigarettes per minute. If there are Y boxes of cigarettes in one case, How many cases can Kramer pack in 2 hours?
In the equation 4Y- 3kX = 18, k is a constant and Y equals 42 when X equals 12. What is the approximate value of X when Y equals 36?
George can fill Q cans of paint in 3 minutes. If there are R cans of paint in one gallon, how many gallons can George fill in 45 minutes?
A confectioner decides to sell all of his pastry due to the coming holiday. His pastry goods are equally divided among a group of 28 regular customers. If only 49 customers come to the bakery, each one will receive 6 less pastry goods. How much pastry does the confectioner needs to sell?
A basket of 1430 apples is divided equally among a group of apple lovers. If 45 people join the group, each apple lover would receive 9 apples less. How many apples did each person get before 45 people joined the feast?
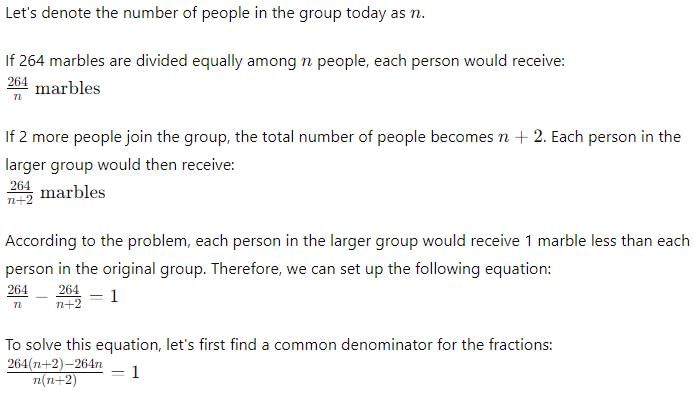
A jar of 264 marbles is divided equally among a group of marble-players. If 2 people join the group, each one would receive 1 marble less. How many people are there in the group today?
How many 3-digit numbers are possible using permutations with repetition allowed if digits are 1-9?
if x and y are positive integers (x>y), what is the units’ digit of (10x – 9y)2 ?
Two brothers took the GMAT exam, the higher score is X and the lower one is Y. If the difference between the two scores is equal to their average, what is the value of Y/X ?
Two people measure each other’s height, the height of the taller person is H and the height of the other person is L. If the differences in their height is equal to their average height, what is the Value of H/L ?