Test: Electromagnetic Induction - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electromagnetic Induction - 2
A flux of 1m Wb passes through a strip having an area A = 0.02 m2. The plane of the strip is at an angle of 60º to the direction of a uniform field B. The value of B is
The number of turns in a long solenoid is 500. The area of cross-section of solenoid is 2 × 10-3 m2. If the value of magnetic induction, on passing a current of 2 amp, through it is 5 × 10-3 tesla, the magnitude of magnetic flux connected with it in webers will be
A conducting loop of radius R is present in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular the plane of the ring. If radius R varies as a function of time `t', as R = R0 + t. The e.m.f induced in the loop is
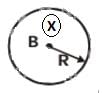

The instantaneous flux associated with a closed circuit of 10Ω resistance is indicated by the following reaction f = 6t2 _ 5t + 1, then the value in amperes of the induced current at t = 0.25 sec will be
When a magnet is being moved towards a coil, the induced emf does not depend upon
An electron is moving in a circular orbit of radius R with an angular acceleration a. At the centre of the orbit is kept a conducting loop of radius r, (r < < R). The e.m.f induced in the smaller loop due to the motion of the electron is
A field of 5 x 104/p ampere-turns/metre acts at right angles to a coil of 50 turns of area 10-2 m2. The coil is removed from the field in 0.1 second. Then the induced emf in the coil is
square wire loop of 10.0 cm side lies at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of 20T. A 10 V light bulb is in a series with the loop as shown in the fig. The magnetic field is decreasing steadily to zero over a time interval Dt. The bulb will shine with full brightness if Dt is equal to
The rate of change of magnetic flux denisty through a circular coil of area 10-2 m2 and number of turns 100 is 103 Wb/m2/s. The value of induced e.m.f. will be
A long solenoid contains 1000 turns/cm and an alternating current of peak value 1A is flowing in it. A search coil of area of cross-section 1 × 10-4 m2 and having 50 turns is placed inside the solenoid with its plane perpendicular to the axis of the solenoid. A peak voltage of 2p2 × 10-2V is produced in the search coil. The frequency of current in the solenoid will be
In an iron cored coil the iron core is removed so that the coil becomes an air cored coil. The inductance of the coil will
The magnetic flux through a stationary loop with resistance R varies during interval of time T as f = at (T _ t). The heat generated during this time neglecting the inductance of loop will be
The dimensions of permeability of free space can be given by
A closed planar wire loop of area A and arbitrary shape is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B, with its plane perpendicular to magnetic field. The resistance of the wire loop is R. The loop is now turned upside down by 180° so that its plane again becomes perpendicular to the magnetic field. The total charge that must have flowen through the wire ring in the process is
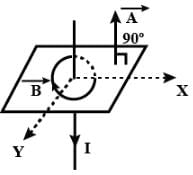
A square coil ABCD is placed in x-y plane with its centre at origin. A long straight wire, passing through origin, carries a current in negative z-direction. Current in this wire increases with time.The induced current in the coil is
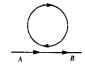
Two identical coaxial circular loops carry a current i each circulating in the same direction. If the loops approach each other
In the arrangement shown in given figure current from A to B is increasing in magnitude. Induced current in the loop will
The north pole of a magnet is brought near a coil. The induced current in the coil as seen by an observer on the side of magnet will be
A metal sheet is placed in a variable magnetic field which is increasing from zero to maximum. Induced current flows in the directions as shown in figure. The direction of magnetic field will be -
A small conducting rod of length l, moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B as shown in fig-
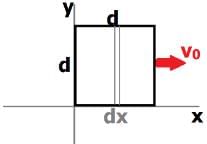
The magnetic field in a region is given by . A square loop of edge-length d is placed with its edge along x & y axis. The loop is moved with constant velocity
. The emf induced in the loop is
Consider the situation shown in fig. The resistanceless wire AB is slid on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire AB is replaced by a resistanceless semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will
A conducting square loop of side I and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A uniform and constant magnetic field B exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the loop in fig. The current induced in the loop is
Two identical conductors P and Q are placed on two frictionless fixed conducting rails R and S in a uniform magnetic field directed into the plane. If P is moved in the direction shown in figure with a constant speed, then rod Q
Two infinitely long conducting parallel rails are connected through a capacitor C as shown in the figure. A conductor of length l is moved with constant speed v0. Which of the following graph truly depicts the variation of current through the conductor with time ?
A thin wire of length 2m is perpendicular to the xy plane. It is moved with velocity through a region of magnetic induction
Wb/m2. Then potential difference induced between the ends of the wire
A long metal bar of 30 cm length is aligned along a north south line and moves eastward at a speed of 10 ms-1. A uniform magnetic field of 4.0 T points vertically downwards. If the south end of the bar has a potential of 0V, the induced potential at the north end of the bar is
A conducting rod moves with constant velocity v perpendicular to the long, straight wire carrying a current I as shown compute that the emf generated between the ends of the rod.
A square loop of side a and resistance R is moved in the region of uniform magnetic field B (loop remaining completely insidefield), with a velocity v through a distance x. The work done is
A rod closing the circuit shown in figure moves along a U shaped wire at a constant speed v under the action of the force F. The circuit is in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane. Calculate F if the rate of heat generation in the circuit is Q.



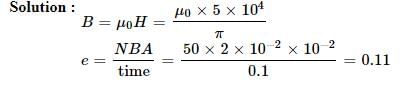
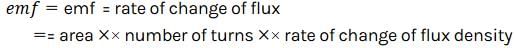
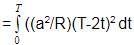
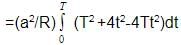
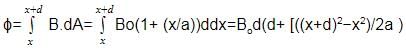
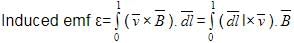
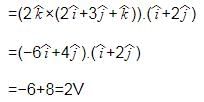
 )
)
















