CTET Practice Test: Child Pedagogy-5 - CTET & State TET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - CTET Practice Test: Child Pedagogy-5
Which of the following factors is not related to motivation?
Abraham Maslow explained theory of motivation in 1954 in the perspective of
Safety need refers to the protection of the organism from his enemies of the environment. These enemies may be
A child is discarded in the class because of his handicap. Which of the following needs will have to be fulfilled by the teacher to motivate him for learning?
If a child doesn’t concentrate in study then what should do the teacher?
To develop correct pronunciation in children teacher should
Children should have knowledge of grammar because
The CAVD test consists of four parts, namely, sentence completion, arithmetical reasoning, vocabulary and –
To start the work, continue and stable, it is called
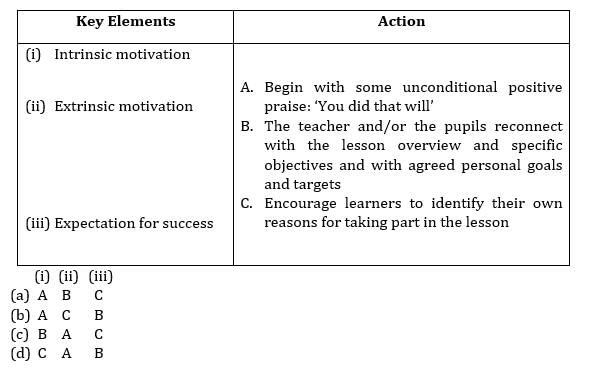
With the reference to activities relating to the issue of motivation match the following.
A student works hard to clear an entrance test for admission into a medical college. The student is said to be motivated
Role of a teacher is necessary for the development of
…………. is considered a sign of motivated teaching?
Which of the following is not necessary while giving home work to pupils?
Which of the following points is taken in account while using black board in the class?
All of the following are needed to achieve learning objectives except















