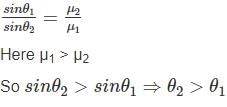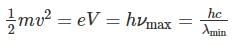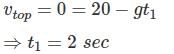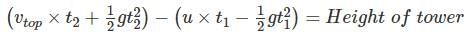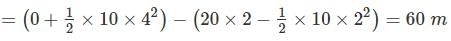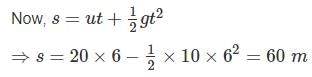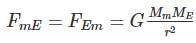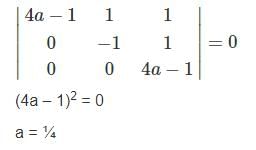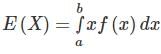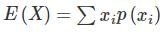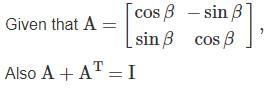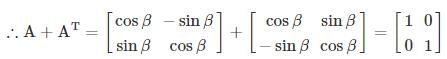Full Test 3 - EKT CSE - AFCAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Full Test 3 - EKT CSE
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A light ray passing through the glass from denser to rarer medium. Which of the following diagram is correct?
In an x-ray tube, the electron strikes the target with energy E and the characteristic wavelength is λ. If the energy of electron increased then then wavelength of the characteristic x-ray λ is
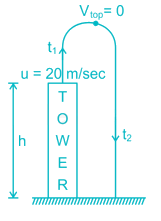
A ball thrown vertically upward with a speed of 20 m/sec from the top of a tower returns to the earth in 6 sec. The height of the tower (take g = 10 m/sec 2) –
The mass of moon is 1% of the mass of earth. The ratio of gravitational pull of earth on moon and that of moon on earth will be
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about HTTP cookies?
The greatest negative number which can be stored in a computer that has 8 bit word length and uses 2’complement arithmetic is
If two numbers in excess-3 code are added and the result is less than 9, then to get equivalent binary
In 8085 B, C, D, E, H and L are called _______ 8 – bit registers.
A J – K flip flop can be made from and S – R flip flop by using two additional
The system of linear equations
(4a – 1)x + y + z = 0
-y + z = 0
(4a – 1) z = 0
has a non-trivial solution, if a equals
f ‘X’ is a continuous random variable, then the expected value is given by (where p(x) is the probability function)
A car of mass 1000 kg travelling at 32 ms-1 dashes into the rear of a truck of mass 8000 kg moving in the same direction with a velocity of 4 ms-1. After the collision, the car bounces back with a velocity of 8 ms-1. What is the velocity of the truck after the impact?
If ω is a cube root of unity then the value of (1−ω8)(1−ω4)(1−ω2)(1−ω) is ___
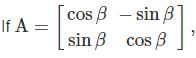 then the sum of matrix A and its Transpose is equal to unity matrix then the value of β is
then the sum of matrix A and its Transpose is equal to unity matrix then the value of β is
The widely employed computer architecture for CAD/CAM application