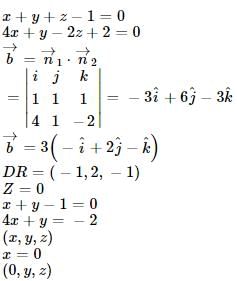JEE Advanced Level Test: Three Dimensional 3D Geometry- 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Level Test: Three Dimensional 3D Geometry- 3
Equation of plane which passes through the point of intersection of l ines 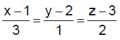 and
and 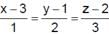 and at greatest distance from the point (0, 0, 0) is
and at greatest distance from the point (0, 0, 0) is
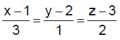 and
and 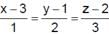 and at greatest distance from the point (0, 0, 0) is
and at greatest distance from the point (0, 0, 0) isThe base of the pyramid AOBC is an equilateral triangle OBA with each side equal to 4√2, 'O'is the origin of reference, AC is perpendicular to the plane of Δ OBC and 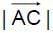 = 2. Then the cosine of the angle between the skew straight lines one passing through A and the mid point of OB and the other passing through O and the mid point of BC is
= 2. Then the cosine of the angle between the skew straight lines one passing through A and the mid point of OB and the other passing through O and the mid point of BC is
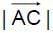 = 2. Then the cosine of the angle between the skew straight lines one passing through A and the mid point of OB and the other passing through O and the mid point of BC is
= 2. Then the cosine of the angle between the skew straight lines one passing through A and the mid point of OB and the other passing through O and the mid point of BC isIn the adjacent figure ‘P’ is any arbitrary interior point of the triangle ABC such that the lines AA1,BB1,CC1 are concurrent at P. Value of 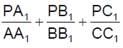 is always equal to
is always equal to
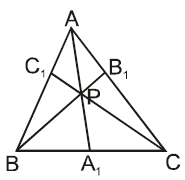
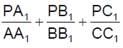 is always equal to
is always equal toA tetrahedron has vertices at O(0, 0, 0), A(1, 2, 1), B(2, 1, 3) and C(–1, 1, 2). Then the angle between the face OAB and ABC will be
The two lines x = ay + b, z = cy + d and = a' y + b', z = c' y + d' will be perpendicular, iff
ABC is a triangle where A = (2, 3, 5), B = (–1, 2, 2) and C(λ, 5, μ). If the median through A is equally inclined to the axes then
A mirror and a source of light are situated at the origin O and at a point on OX, respectively. A ray of light from the source strikes the mirror and is reflected. If the D.r.’s of the normal to the plane are 1, –1, 1, then D.C.’s of the reflected ray are
The equation of motion of a point in space is x = 2t, y = –4t, z = 4t where t measured in hours and the co-ordinates of moving point in kilometers. The distance of the point from the starting point O(0, 0, 0) in 10 hours is
Minimum value of x2 + y2 + z2 when ax+by+cz = p is
The direction cosines of a line equally inclined to three mutually perpendicular lines having ℓ1, m1, n1, ; ℓ2, m2, n2 ; ℓ3, m3, n3 are
The co-ordinates of the point where the line joining the points (2, –3, 1), (3, –4, –5) cuts the plane 2x + y + z = 7 are
If the line joining the origin and the point (–2, 1, 2) makes angle θ1 ,θ2 and θ3 with the positive direction of the coordinate axes, then the value of cos 2θ1 + cos 2θ2 + cos 2θ3 is
The square of the perpendicular distance of point P(p, q, r) from a line through A(a, b, c) an whose direction cosine are (ℓ) , m, n is
Equation of the plane passing through A(x1, y1, z1) d containing the line 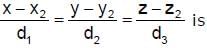
The equation of the line x + y + z – 1 = 0, 4x + y – 2z + 2 = 0 written in the symmetrical form is
The acute angle that the vector 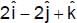 makes with the plane contained by the two vectors
makes with the plane contained by the two vectors 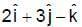 and
and 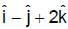 is given by
is given by
The ratio in which the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 504 divides the line joining the points (12, –4, 8) and (27, –9, 18) is
The equation of the planes through the origin which are parallel to the line 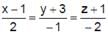 and distance 5/3 from it are
and distance 5/3 from it are
If the edges of a rectangular parallelopiped are 3, 2, 1 then the angle between a pair of diagonals is given by
Consider the lines x/2 = y/3 = z/5 and x/1 = y/2 = z/3 equation of the line which
The direction cosines of the lines bisecting the anglebetween the lines whose direction cosines are ℓ1, m1, n1 and ℓ2, m2, n2 and the angle between these lines is 0, are
The equation og line AB is  . Through a point P(1, 2, 5), line PN is drawn perpendicular to AB and line PQ is drawn parallel to the plane 3x + 4y + 5z = 0 to meet AB is Q. Then
. Through a point P(1, 2, 5), line PN is drawn perpendicular to AB and line PQ is drawn parallel to the plane 3x + 4y + 5z = 0 to meet AB is Q. Then
The planes 2x – 3y – 7z = 0, 3x – 14y – 13z = 0 and 8x – 31y – 33z = 0
If the length of perpendicular drawn from origin on a plane is 7 units and its direction ratios are –3, 2, 6, then that plane is
Let a perpendicular PQ be drawn from P(5, 7, 3) to the line 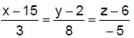 when Q is the foot.
when Q is the foot.
Then