Current Electricity MSQ - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Current Electricity MSQ
A battery of internal resistance 2Ω is connected to a variable resistor whose value can vary from 4Ω to 10Ω. The resistance is initially set at 4Ω. If the resistance is now increased then, which of the statement is not correct.
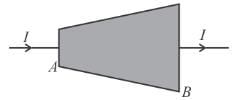
In the figure a conductor of non-uniform cross-section is shown. A steady current I flows in it.

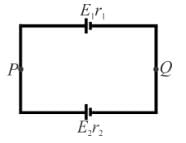
Two cells of unequal emfs E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are joined as shown in figure. VP and VQ are the potential at P and Q respectively.

A conductor of truncated conical (frustum) is connected to a battery of emf ∈ as shown in the figure.
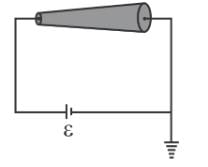
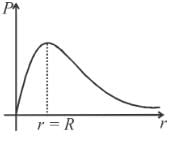
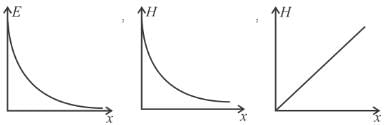
If at a section distance x from left end, electric field intensity, potential and rate of generation of heat per unit length are E, V and H respectively, then which of the following graphs(s) is/are correct?
A variable current flows through a 1Ω resistor for 2 seconds. Time dependence of the current is shown in the graph.

Consider a resistor of uniform cross sectional area connected to a battery of zero internal resistance. If the length of the resistor is doubled by stretching it then :
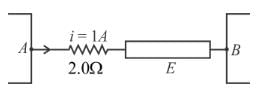
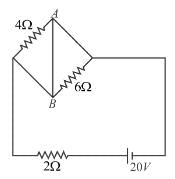
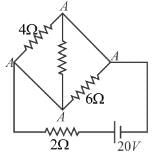
AB is part of a circuit as shown, that absorbs energy at a rate of 50W. E is an emf device that has no internal resistance.
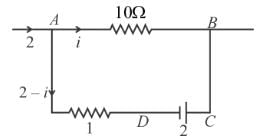
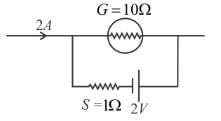
The galvanometer shown in the figure has resistance 10Ω. It is shunted by a series combination of a resistance S = 1Ω and an ideal cell of emf 2V. A current 2A passes as shown.



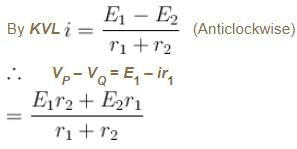
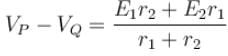
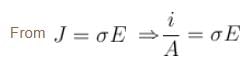
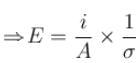 as i and σ are same for all cross-section
as i and σ are same for all cross-section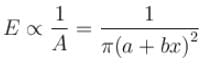
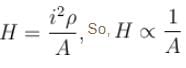
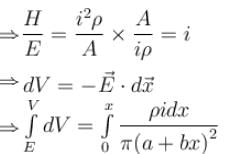
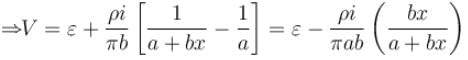
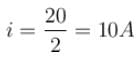
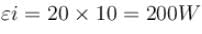
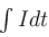 = Area under the curve = 10C
= Area under the curve = 10C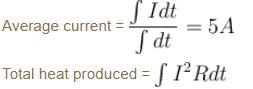
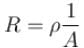 becomes four times the previous value. Hence after the wire is elongated the current becomes one fourth. Electric field is potential difference per unit length and hence becomes half the initial value. The power delivered to resistance is
becomes four times the previous value. Hence after the wire is elongated the current becomes one fourth. Electric field is potential difference per unit length and hence becomes half the initial value. The power delivered to resistance is 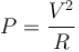 and hence becomes one fourth.
and hence becomes one fourth. VAB·I = 50W
VAB·I = 50W