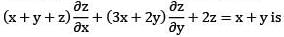Partial Differential Equation MCQ - 1 - IIT JAM MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Partial Differential Equation MCQ - 1
The order of equation p tan y + q tan x = sec2z is
Which of the following is one of the criterions for linearity of an equation?
For a partial differential equation, in a function φ (x, y) and two variables x, y, what is the form obtained after separation of variables is applied?
The general solution of (y — z)p + (z — x)q = x — y is
The integral surface to the first order p. d. e 2 y (z — 3) 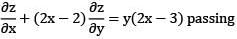 through the curve x2 + y2 = 2x, z = 0 is
through the curve x2 + y2 = 2x, z = 0 is
Complete integral for the partial differential equation z = px + gy — sin(pq) is
The general integral of the partial differential equation (y + z x) zx — (x + yz)Zy = x2 — y2 is
The complete integral of q(p — cosx) = cosy
Consider the following statement about the following p. d. e. p + q — pq = 0
(i) it has no singular solutions
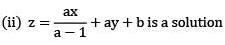
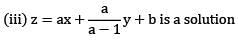
(iv) It is a first order non — linear p. d. e. Then choose the
correct code.
Integral surface of (2x y — l)p + (z — 2x2)q = 2(x — yz) passing through the line x0 (s) = 1 y0(s) = 0 z0(s) = s
Integral surface of PDE x2p + y2q = —z2 which passes through hyperbola xy = x + y, z = 1 is given by
Consider 4xyz = pq + 2px2y + 2qxy2
(i) It can be reduced to Claerut's form by some suitable transformation.
(ii) z = ax + by + ab is complete integral
(iii) z = —x2y2 is singular solution choose correct code.


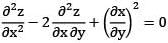 is of the order
is of the order