Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Chemical Kinetics) - JEE MCQ
27 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Chemical Kinetics)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-24) This section contains 24 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
At a given temperature k1 = k2 for the reaction,
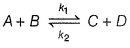
For which case, a steady state is obtained?
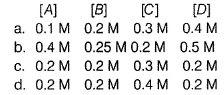
In the reaction, 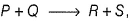 the time taken for 75% reaction of P is twice the time taken for 50% reaction of P. The concentration of Q varies with the reaction time as shown in the figure. The overall order of the reaction is
the time taken for 75% reaction of P is twice the time taken for 50% reaction of P. The concentration of Q varies with the reaction time as shown in the figure. The overall order of the reaction is
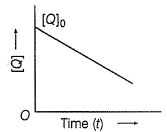
[JEE Advanced 2013]
The time for half-life period of a certain reaction, A → Products is 1 h. When the initial concentration of the reactant A is 2.0 mol L-1, how much time does it take for its concentration to come from 0.50 to 0.25 mol L-1, if it is a zero order reaction?
[AIEEE 2010]
A radioactive substance decays 20% in 10 min. If at the start, there are 5 x 1020 atoms present, after what time will the number of atoms be reduced to 5 x 1017 atoms?
Rate constant of a reaction with a virus is 3.3 x 10-4 s-1. Time required for a virus to become 75% inactivated is
For the first order reaction, total pressure is 350 mm after 30 min and 500 mm after complete reaction. Thus, rate constant is
t1/A can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 3/4 of the initial value. If the rate constant for a first order reaction is k, then t 1/4 can be written as
For the following first order gaseous phase reaction,
time taken for acetone vapour pressure to drop to 0.30 atm from 2 atm is
The rate constant for a first order reaction is 60 s-1. How much time will it take to reduce the initialconcentration of the reactant to its (1/16)th value?
The half-life of a reaction was doubled when initial concentration was doubled. Thus, order of the reaction is
Rate law of the reaction A → product is
rate = k[A]
Graphically, it is represented as
Hence, rate constant is
For the non-stoichiometric reaction, the following kinetic data were obtained in three separate experiments, all at 298 K.
Q.
The rate law for the formation of C is
A hydrogenation reaction is carried out at 500 K.
Q.
If rate remains constant, then Ea is
Rate of a particular reaction increases by a factor 2 when the temperature is increased from 27°C to 37°C. Hence, activation energy of the reaction is
Interconversion of boat form to chair form of cyclohexane is first order (in both sides).
Equilibrium constant, Kc =104
Also, energy of activation of conversion of chair to boat form is 42 kJ mol-1 in the following equation
Q.
Observed reaction rate constant at 298 K is
In the reaction,
if we start with [A]0 = 10 M , then after one natural life time, concentration of A decrea sed to
Number of natural life times (Tav ) required for a first order reaction to achieve 99.9% level of completion is
For the reaction,
rate law is
Q.
At the start, pressure is 100 mm and after 10 min, pressure is 120 mm. Thus, rate constant (in min-1) is
Q.
HA and HB are two strong acids. Relative strength of strong acids is
Initial concentration of A = 2M and after 10 min, reaction is 10% completed. Thus, half-life period is
The decomposition of N2O to N2 and O2 follow s rate law in gaseous phase as
Q.
At 1000 K, half-life of the reaction is 3.58 x 103 min. Starting with initial pressure of N2O as 2.20 atm, total pressure after one half-life is
The rate of a first order reaction is 0.04 mol L-1 s-1 at 10 min and 0.03 mol L-1 s-1 at 20 min. Thus , half-life of the reaction is
For the non-equilibrium process,
the rate is first order w.r.t. A and second order w.r.t. B.
When [A]= 1.0 M, [B]= 1.0 M, rate = 1.0x 10-2 M s-1
When 50% of each of reactant has been converted into products, rate is
For a reaction of the type
[X]0 is the concentration of X at time t = 0 and [X] is the concentration of X at time t = t
Thus, correct rate expression is
Direction (Q. Nos. 25-27) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The rate of chemical reaction generally increases rapidly for a small temperature increase.
Statement II : Increase in temperature increases fraction of molecules with energies in excess of activation energy.
Statement I : For a certain reaction, large fraction of molecules has energy more than the threshold energy,yet the rate of reaction is very slow.
Statement II : Collisions are only effective if they have proper orientation. In the absence of proper orientation rate becomes, slow.
Statement I : Certain reactions are thermodynamically feasible but their rates are very slow.
Statement II : Energy of activation may be high for such reactions.














