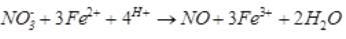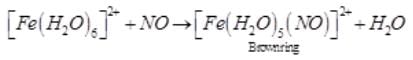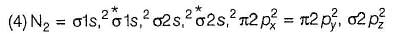Test: General Properties of Group-15 (Nitrogen & Phosphorus) - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Properties of Group-15 (Nitrogen & Phosphorus)
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
Correct order of 2nd ionisation energy of C, N, O and F is
Which trend enthalpy is correct ?
Boiling Point of liquid nitrogen is
Oxidation of ammonia with CuO produce a gaseous chemical which can also be obtained by:
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?
Which is the correct order w.r.t the given property?
The ratio of bond pairs and lone pairs in a P4 molecule is
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Regarding black phosphorus correct statements are:
Which are correct statements ?
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is
The correct statements among the given are :
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing the theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
Phosphorus was discovered by Brand (1669), Scheele isolated from bone ash and Lavoisier proved its elemental nature (1777). The principal minerals are phosphate rock, fluoroacetate, and chloroacetate. Phosphorus is prepared by the direct reduction of phosphorite by carbon in the presence of silica. It exists in different allotropic forms such as yellow or white, red, a-black,f3-black, etc. White P is most reactive, poisonous, glows in dark, and readily catches fire due to unstable discrete P4 molecules. Red P is inert, non-poisonous, does not glow, etc., due to its polymeric structure. a-black, f3 -black allotropes are also chemically inert, do not ignite at normal temperature. It has a layer structure like graphite and acts as a conductor.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Passage
Phosphorus was discovered by Brand (1669), Scheele isolated from bone ash and Lavoisier proved its elemental nature (1777). The principal minerals are phosphate rock, fluoroacetate, and chloroacetate. Phosphorus is prepared by the direct reduction of phosphorite by carbon in the presence of silica. It exists in different allotropic forms such as yellow or white, red, a-black,f3-black, etc. White P is most reactive, poisonous, glows in dark, and readily catches fire due to unstable discrete P4 molecules. Red P is inert, non-poisonous, does not glow, etc., due to its polymeric structure. a-black, f3 -black allotropes are also chemically inert, do not ignite at normal temperature. It has a layer structure like graphite and acts as a conductor.
Q. The allotrope of phosphorus with low ignition temperature is:
Passage
Phosphorus was discovered by Brand (1669), Scheele isolated from bone ash and Lavoisier proved its elemental nature (1777). The principal minerals are phosphate rock, fluoroacetate, and chloroacetate. Phosphorus is prepared by the direct reduction of phosphorite by carbon in the presence of silica. It exists in different allotropic forms such as yellow or white, red, a-black,f3-black, etc. White P is most reactive, poisonous, glows in dark, and readily catches fire due to unstable discrete P4 molecules. Red P is inert, non-poisonous, does not glow, etc., due to its polymeric structure. a-black, f3 -black allotropes are also chemically inert, do not ignite at normal temperature. It has a layer structure like graphite and acts as a conductor.
Q. The allotrope of phosphorus that has layer lattice-like graphite is:
Matching List Type
Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c), and (d), out of which one is correct
Match column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below:
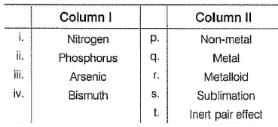
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below :
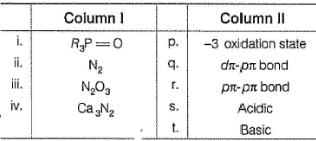
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of
Number of chemical species having negative oxidation state for nitrogen among
NF3, NCI3, NH2OH, NH3,CH3NH2, NH-2, L13N, N20, HCN, HNC, NO-2
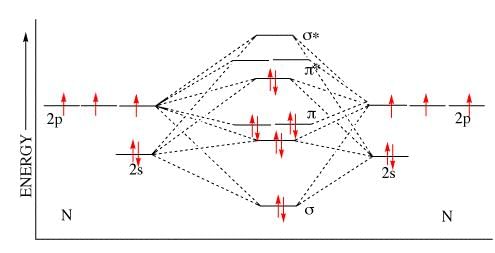
According to molecular orbital theory, number of electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Statement I: N2 is less reactive than P4.
Statement II: Nitrogen has more electron gain enthalpy than phosphorus.



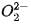 contains all paired electrons and are diamagnetic in nature.
contains all paired electrons and are diamagnetic in nature.