Test: Nitrogen & Phosphorus Compounds - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Nitrogen & Phosphorus Compounds
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-7) This section contains 7 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
The hybridisation of N in solid state for N2O5 is
PH3 becomes spontaneously inflammable due to the presence of
Which is incorrect among the following options?
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively
Which is the correct order of basic strength ?
Solid PCl5 and solid PBr5 exist respectively as
Number of moles of NaOH needed to neutralise one mole each of H3PO2, H3PO3 and H3PO4 respectively are
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?
Acetamide can be converted to methenamine by which of the following reactions?
Which of the correct statement for the given acids?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
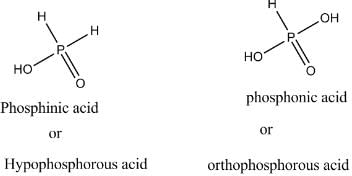
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:
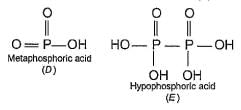
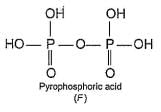
Q.
Although metaphosphoric acid is written as a monomer, it exists as a polymer (HPO3)n. The number of P—O—P bonds in cyclic trimetaphosphoric acid is
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:


Q.
Which of the acids show reducing properties?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
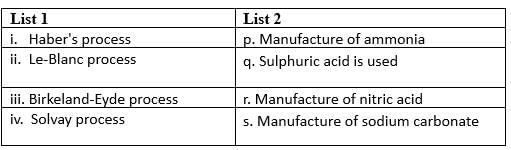
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-19) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Number of chemical species having bond between nitrogen atoms
N2O4, N2O5, N2H4, N2O , N2O3, NH4NO3, H2N2O2
Number of metals that show passivity with cone. HNO3 among Cr, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn Al, Ag, Sn.
2H3PO2 → H3PO4 + PH3 in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
Direction (Q. No. 20) This section is bassed on Statment I and Statment II. II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3
Statement II : NF3 ionises to give F- ions in aqueous solutio