Olympiad Test: Matter - 2 - Class 5 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Matter - 2
Which change of state occurs when particles in a solid begin to move slowly past each other?

Directions: Fill up the grid by answering the following questions.
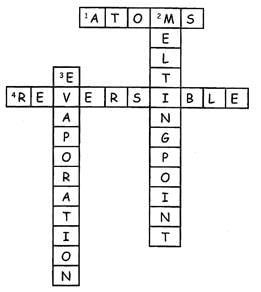
(Across 4) In physical changes, the state changes but the main thing remains the same. This change can be converted back to its original form and thus is called

(Across 4) In physical changes, the state changes but the main thing remains the same. This change can be converted back to its original form and thus is called
Directions: Fill up the grid by answering the following questions.
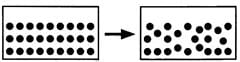
(Down 3) Which process is depicted in the following figure? _____________



Directions: Fill up the grid by answering the following questions.
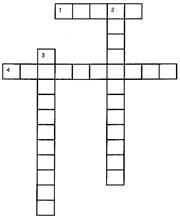
(Down 2) The temperature at which the solid gets converted into a liquid ___.
Directions: Fill up the grid by answering the following questions.
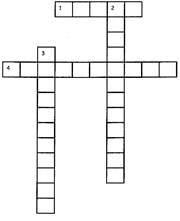
(Across 1) These are the small particles of which the matter is made up of ___.
Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Statement A: Physical change is irreversible.
Statement B: Chemical change is irreversible.
Why can't we make statue of water?
A: Liquid can't have its own shape.
B: It is hard to change shape of water like iron.
The diagram given below depicts which of the processes of the change of state of matter?

Which of the following takes place when water vapour changes into ice?