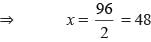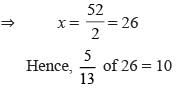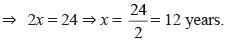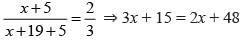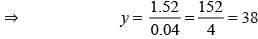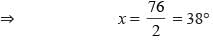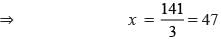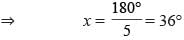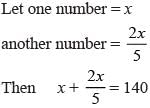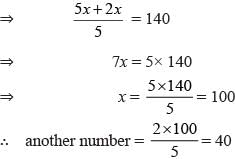Olympiad Test: Linear Equations In One Variable - 2 - Class 7 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Linear Equations In One Variable - 2
The sum of two consecutive even number is 98. What is the smaller number?
On adding nine to the twice of a whole number gives 61. What is 5/13 of that whole number?
After 12 years Manish will be three times as old as he was 4 years ago. What is his present age?
Niraj is 19 years younger than his cousin after 5 years their age will be in the ratio 2:3. What is the present age of Niraj?
What is the value of p in the given equation 8(2p – 5) – 6(3p – 7) = 1?
What is the value of y in the given equation 0.6 y + 0.8 = 0.56y + 2.32?
Two complementary angles are differ by 14°. What is the measure of larger angle?
The sum of three consecutive odd numbers is 147. What is the smallest odd number?
In an isosceles triangle, the vertex angle is thrice of its base angle. What is the measure of vertex angle?
A number is 2/5 times of another number. If their sum is 140, find the larger number.