Olympiad Test: Animal Life -1 - Class 4 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Animal Life -1
A student observed that birds sit on their eggs before the eggs hatch into young ones. The reason is to:
Which of the following are most similar to tadpoles?
What does the egg yolk contain that gives energy to the embryo?
At which stage does the organism cover itself in a cocoon?
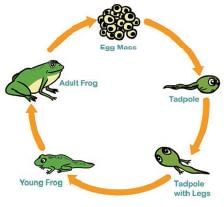
The following diagram represents the life cycle of a frog.
Answer the following questions based on this diagram:
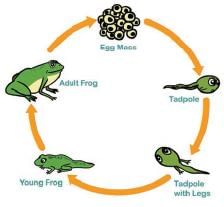
Q. A tadpole resembles:
The following diagram represents the life cycle of a frog.
Answer the following questions based on this diagram:

Q. Which of the following is possessed by the tadpole but not the adult frog?
The following diagram represents the life cycle of a frog.
Answer the following questions based on this diagram:
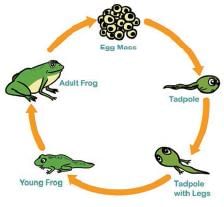
Q. A dolphin is:
The following diagram represents the life cycle of a frog.
Answer the following questions based on this diagram:
Q. Eggs of the fish are called:
Which of the following sets consists of only mammals?















