Olympiad Test: Matter And Materials -1 - Class 4 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Matter And Materials -1
The amount of space taken up by matter is called:
Which of the following is/are in a liquid state normally?
Which of the following states of matter has the strongest forces of attraction between its molecules?
The bubbles that come out rapidly when we open a soda water bottle are:
Which of the following has a fixed volume but no fixed shape?
The three different containers shown below contain 500 ml of water.
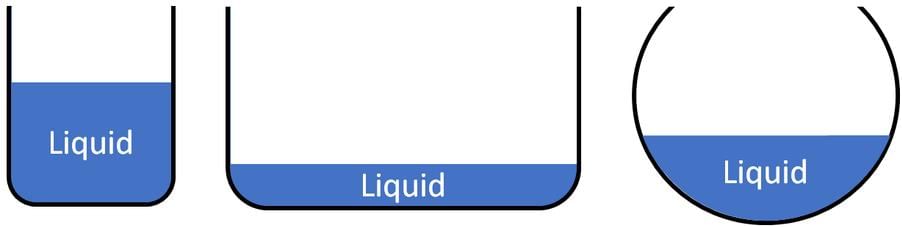
Q. This indicates that water has _______________.
Sunil took some water and dissolved some salt in it. Later he placed the salty water under sunlight for four days. He found only the crystals of salt but not the water. The process demonstrated in the above experiment is:
Look at the given pictures carefully. They show particles of the same matter. In which picture is the matter closet?
Which of the following is incorrectly written?
The object in the given figure is made of a combination of_______________ and __________________.

Which of the following objects is incorrectly classified?

The homogeneous mixture of two or more substances is called:
When gas changes into liquid, it is called:
One day Surya’s father put naphthalene balls between woolen clothes to keep them protected from insects. After a few days he saw that the size of the naphthalene balls had reduced. This process is called:














