Test: Physical & General Properties of Alkyl Halides - JEE MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Physical & General Properties of Alkyl Halides
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
What is the major product of the reaction?

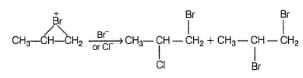
Which are the products of the following sequence of reaction?
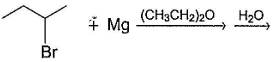
What is the product of the reaction shown?
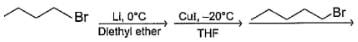

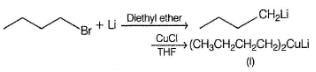
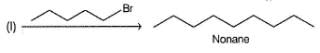
What set of reagents can be used to make octane from butyl chloride?
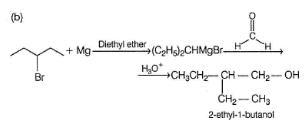
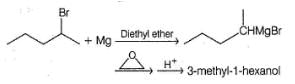
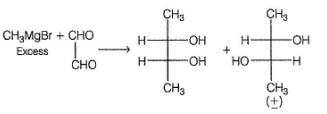
Which of the following synthesis give 3-methyl-1 -hexanol?
Q.
What is the product in the above reaction?
Which of the following alkyl halides cannot be converted into Grignard reagents?
Which one is liquid at room temperature?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-14) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
1-chlorobutane can be reduced to butane by
Tertiary butyl chloride can be reduced to 2-methyl propane by
Which of the following float over water?
Which of the following halides are not suitable for Grignard’s synthesis?
What is the expected product in the following reaction?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
In alkyl halides C—X bond is polar. Polarity of C—X bond is responsible for several characteristic reactions of alkyl halides viz.
R—X + H- (from metal hydride) → R —H + X-
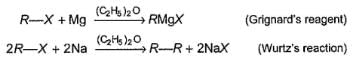
Q.
Which of the following will most easily be reduced by LiAIH4?
Passage
In alkyl halides C—X bond is polar. Polarity of C—X bond is responsible for several characteristic reactions of alkyl halides viz.
R—X + H- (from metal hydride) → R —H + X-
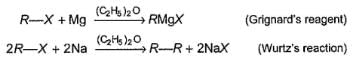
Q.
Which forms Grignard’s reagent with maximum difficulty?
Passage
In alkyl halides C—X bond is polar. Polarity of C—X bond is responsible for several characteristic reactions of alkyl halides viz.
R—X + H- (from metal hydride) → R —H + X-
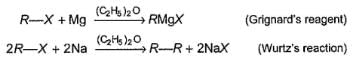
Q.
Which of the following required more than one type of alkyl halides for its preparation by Wurtz’s reaction?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Consider the following reactions,
Q.
How many different diols are formed?
Dichloroalkanes with appropriate skeleton, on refluxing with Na in diethyi ether undergo cyclisation via Wurtz’s reaction. How many different isomeric dibromoalkanes on refluxing with Na metal in diethyl ether can give the same 1,4-dimethyl cyclohexane?
How many of the following are denser than water?
i. CCl4
ii. CH3CH2CH2CH2CI
iii. Bromocyclohexane
iv. Chlorocyclopentane
v. 1 ,3-difiuorocyclopentane
vi. CH3I
vii. 1-fluorodecane
viti. CH2Br2
ix. CH3CI
X. CHCl3
Statement Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 21 and 22) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : CH3F is less polar than CH3CI.
Statement II : F has greater electronegativity than Cl.
Statement I : A tertiary halide (R3CX) is very less likely to form Grignard’s reagent with Mg in THF.
Statement II : Tertiary carbanion are highly unstable, very less likely to be formed.