Test: SN2 Reaction Reactivity - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: SN2 Reaction Reactivity
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c))and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following would be the strongest nucleophile in methanol?
Predict the product in nucleophilic substitution reaction.

Which of the following are the examples of strong nucleophiles but weak base in protic solvents?
I. CH3S-
II. CH3O-
III. I-
IV. H2O
V. F-
The specific rotation of optically pure (R)-2- butanol is -13.52° at 25°C. An optically pure sample of (R)-2- bromobutane was treated with aqueous NaOH in order to form 2-butanol via SN2 reaction. What would be the specific rotation of the product assuming 100% yield?
Which of the following correctly describe the relative nucleophilicities of methoxide and tertiary butoxide ion?
Arrange the following in increasing order of reactivity in an SN2 reaction with K I in acetone solvent.
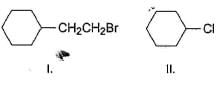
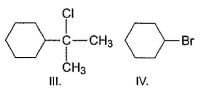
In the following set of nucleophiles, the strongest and the weakest nucleophile respectively are
I. CH3S-
II. CH3COC-
III. HO-
IV. C6H5C-
Which of the following on treatment with NaCN (aq) results in an achiral product?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-17) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
In which of the following pair(s), the first one is stronger nucleophile than the second one?
In which of the following pair(s), the first one is better leaving group than the second one?
In which of the following reaction, inversion of configuration at chiral carbon takes place?
Consider the following SN2 reaction,
1-bromobutane + NaCN(aq) → pentanenitrile +NaBr
Q.
Which of the following solvents) when replaces water in the above reaction, increases the rate?
In which of the following reaction(s), reactant and product are correctly matched?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-23) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
In a SN2 reaction, solvent plays a very important role. Hydroxylic solvents like water, alcohols, carboxylic acids etc., solvate nucleophile, decreases its reactivity in the reaction.
Size of donor atom of nucleophile also affect nucleophilicity. A larger donor atom is more easily polarised and less solvated, hence a stronger nucleophile. Therefore, in a given group of periodic table, nucleophilicity increases down the group. However solvation effect is more predominant than polarisability.
Q.
In water, the order of nucleophilicity of halides is
Passage I
In a SN2 reaction, solvent plays a very important role. Hydroxylic solvents like water, alcohols, carboxylic acids etc., solvate nucleophile, decreases its reactivity in the reaction.
Size of donor atom of nucleophile also affect nucleophilicity. A larger donor atom is more easily polarised and less solvated, hence a stronger nucleophile. Therefore, in a given group of periodic table, nucleophilicity increases down the group. However solvation effect is more predominant than polarisability.
Q.
In dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) solvent, the order of nucleophilicity of haiides ion is
Passage I
In a SN2 reaction, solvent plays a very important role. Hydroxylic solvents like water, alcohols, carboxylic acids etc., solvate nucleophile, decreases its reactivity in the reaction.
Size of donor atom of nucleophile also affect nucleophilicity. A larger donor atom is more easily polarised and less solvated, hence a stronger nucleophile. Therefore, in a given group of periodic table, nucleophilicity increases down the group. However solvation effect is more predominant than polarisability.
Q.
Which of the following describe correctly the role of H2O a s solvent in a SN2 reaction?
Passage II
In a SN2 reaction, back side attack takes place which leads to inversion of configuration ata-carbon which is known as Walden’s inversion :
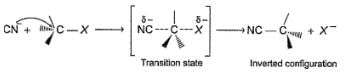
Q.
What is true regarding the follow ing reaction?
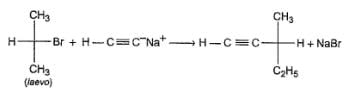
Passage II
In a SN2 reaction, back side attack takes place which leads to inversion of configuration ata-carbon which is known as Walden’s inversion :

Q.
What can be correctly predicted regarding product of the following reaction ?
Passage II
In a SN2 reaction, back side attack takes place which leads to inversion of configuration ata-carbon which is known as Walden’s inversion :

Q.
What can be predicted correctly about product of the following SN2 reaction?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 24 and 25) This section contains 2 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 {both inclusive).
Q.
How many of the following reactions fail to give major product by SN2 reaction as indicated?
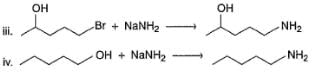
v . H—C≡C—CH2—CH2I + CH3MgBr → H—C ≡C— CH2— CH2— CH3
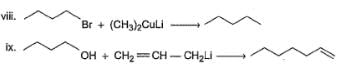
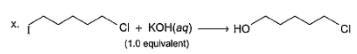
In the following reaction,
Q.
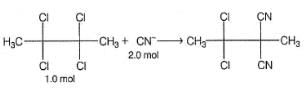
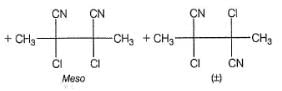
How many different dicyano products are expected?