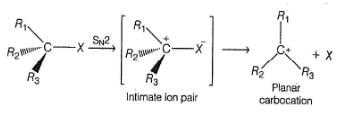
Test: SN1 Reactions - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: SN1 Reactions
In SN1 reaction, racemisation occurs if the reaction occurs at a stereogenic centre, however, 50:50 mixture of enantiomers are rarely obtained, why?
Pick out the compound which reacts fastest in the presence of AgNO3.
From the following, pick out the explanation for why molecule Y hydrolyses faster than molecule Z.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true for SN1 reaction?
I. The rate of SN1 reaction depends on concentration of alkyl halide
II. The rate of SN1 reaction depends on concentration of nucleophile
III. SN1 reactions of alkyl halides are favoured by non-polar solvents
Pick out the following factor(s) which promote a SN1 reaction :
I. Temperature
II. Concentration of nucleophile
III. Concentration of alkyl halide
IV. Aprotic solvents
Which of the following alkyl halides is respectively most and least electrophilic in SN1 reaction?
Rank the following molecules increasing in order of relative rate of SN1 solvolysis with methanol and heat.
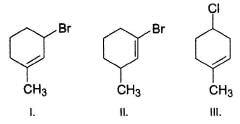
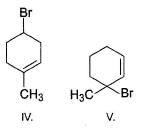
What is the correct order of reactivity of the followings in hydrolysis reaction at elevated temperature?
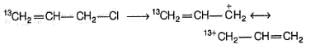
Statement I : When 3-bromo propene, which contain a labelled 13C at C-1 position is refluxed with methanol, following products were obtained.
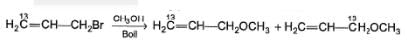
Statement II : Methanol has an acidic proton bonded to oxygen.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-22) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
What is/are true regarding a SN1 reaction?
If a pure dextrorotatory enantiomer of the substrate of the following reaction is boiled with water, the correct statement(s) regarding SN1 product(s) is/are
Which of the following can catalyse the following SN1 reaction?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 23-27) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Five questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
A chemist isolated a compound A with molecular formula C7H13Br. A undergoes very fast SN1 reaction. Spectroscopic evidence indicated that compound A has the following structural characteristics : It contains five sp3-hybridised carbon atoms. Among those five sp3 carbon atoms, three are methyl groups, one CH2 group and one CH group.
It also contains two sp2-hybridised carbon atoms. Also there is only one hydrogen atom attached to sp2 carbons.
The compound contains a total of six aliylic hydrogen atoms.
The carbon atom that holds the Br has one H attached to it.
Working Space
When compound A reacts with boiling water, it undergoes a SN1 reaction and produces two principal products B and C. Both B and C are alcohols with their molecular formula C7H14O. Among the two alcohols, B has the —OH group attached to a sp3 carbon atom that has no H -atoms bonded to it.
Q.
How many stereoisomers are possible for A?
A chemist isolated a compound A with molecular formula C7H13Br. A undergoes very fast SN1 reaction. Spectroscopic evidence indicated that compound A has the following structural characteristics : It contains five sp3-hybridised carbon atoms. Among those five sp3 carbon atoms, three are methyl groups, one CH2 group and one CH group.
It also contains two sp2-hybridised carbon atoms. Also there is only one hydrogen atom attached to sp2 carbons.
The compound contains a total of six aliylic hydrogen atoms.
The carbon atom that holds the Br has one H attached to it.
Working Space
When compound A reacts with boiling water, it undergoes a SN1 reaction and produces two principal products B and C. Both B and C are alcohols with their molecular formula C7H14O. Among the two alcohols, B has the —OH group attached to a sp3 carbon atom that has no H -atoms bonded to it.
Q.
What can be said about the isomerism shown by the two alcohols B and C ?
A chemist isolated a compound A with molecular formula C7H13Br. A undergoes very fast SN1 reaction. Spectroscopic evidence indicated that compound A has the following structural characteristics : It contains five sp3-hybridised carbon atoms. Among those five sp3 carbon atoms, three are methyl groups, one CH2 group and one CH group.
It also contains two sp2-hybridised carbon atoms. Also there is only one hydrogen atom attached to sp2 carbons.
The compound contains a total of six aliylic hydrogen atoms.
The carbon atom that holds the Br has one H attached to it.
Working Space
When compound A reacts with boiling water, it undergoes a SN1 reaction and produces two principal products B and C. Both B and C are alcohols with their molecular formula C7H14O. Among the two alcohols, B has the —OH group attached to a sp3 carbon atom that has no H -atoms bonded to it.
Q.
If the starting compound A is brominated in gas phase in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, a tribromide would result from addition of Br2 to . How many different structures of stereoisomers can be drawn for this tribromide?
A chemist isolated a compound A with molecular formula C7H13Br. A undergoes very fast SN1 reaction. Spectroscopic evidence indicated that compound A has the following structural characteristics : It contains five sp3-hybridised carbon atoms. Among those five sp3 carbon atoms, three are methyl groups, one CH2 group and one CH group.
It also contains two sp2-hybridised carbon atoms. Also there is only one hydrogen atom attached to sp2 carbons.
The compound contains a total of six aliylic hydrogen atoms.
The carbon atom that holds the Br has one H attached to it.
Working Space
When compound A reacts with boiling water, it undergoes a SN1 reaction and produces two principal products B and C. Both B and C are alcohols with their molecular formula C7H14O. Among the two alcohols, B has the —OH group attached to a sp3 carbon atom that has no H -atoms bonded to it.
Q.
If the original compound A is treated with LiAIH4 a new compound D(C7H14) would be produced. How many different structure(s) can be drawn for this D ?
A chemist isolated a compound A with molecular formula C7H13Br. A undergoes very fast SN1 reaction. Spectroscopic evidence indicated that compound A has the following structural characteristics : It contains five sp3-hybridised carbon atoms. Among those five sp3 carbon atoms, three are methyl groups, one CH2 group and one CH group.
It also contains two sp2-hybridised carbon atoms. Also there is only one hydrogen atom attached to sp2 carbons.
The compound contains a total of six aliylic hydrogen atoms.
The carbon atom that holds the Br has one H attached to it.
Working Space
When compound A reacts with boiling water, it undergoes a SN1 reaction and produces two principal products B and C. Both B and C are alcohols with their molecular formula C7H14O. Among the two alcohols, B has the —OH group attached to a sp3 carbon atom that has no H -atoms bonded to it.
Q.
If the starting compound A is treated with ethanolic solution of KOH in boiling condition, a further new compound E (C7H12) is produced as major product by E2 elimination reaction. Which of the following statement will be consistent with E?