Test: E2 Reaction Basics - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: E2 Reaction Basics
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Provide the structure of the major organic product which results in the following reaction.

Provide the structure of the major organic product which results in the following reaction.
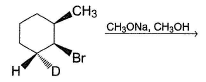
Provide the structure of the major organic product which results in the following reaction.
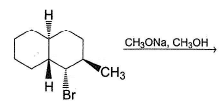
Provide the structure of the major organic product which results in the following reaction.
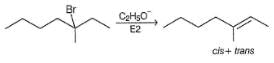
How many distinct alkene products are possible when the alkyl iodide given below undergoes E2 elimination?
Provide the structure of the major organic product given in the following reaction.
Which of the following alkyl halides can produce only a single alkene product when treated with sodium methoxide?
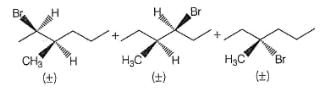
Which of the alkyl chlorides listed below undergoes dehydrohaiogenation in the presence of a strong base to give 2-pentene as the only alkene product?
Which of the following statements is true concerning the E2 reactions of alkyl fluorides?
What is the increasing order of reactivity of the following in an E2 reaction with ethanolic KOH solution?
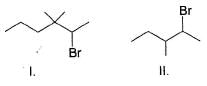
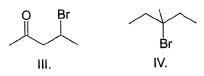
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct statement regarding the above reaction is
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct statement concerning the above reaction is
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct statement concerning the above reaction is
In the reaction the given below,
Q.
The correct statement(s) concerning the above reaction is/are
Consider the following two reactions,
Q.
The correct statement concerning the above reaction is
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-21) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
An alkyl halide X shows diastereomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers. X when treated with KOH solution gives alkene as well as alcohol in comparable amounts by E2 and SN2 reactions respectively. Also, E2 reaction above gives alkene Y as single structural isomer which exists as stereoisomers. The SN2 reaction above produced alcohol Z which show stereoisomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers.
Q.
The structure of X is
Passage I
An alkyl halide X shows diastereomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers. X when treated with KOH solution gives alkene as well as alcohol in comparable amounts by E2 and SN2 reactions respectively. Also, E2 reaction above gives alkene Y as single structural isomer which exists as stereoisomers. The SN2 reaction above produced alcohol Z which show stereoisomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers.
Q.
The correct statement concerning Y is
Passage I
An alkyl halide X shows diastereomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers. X when treated with KOH solution gives alkene as well as alcohol in comparable amounts by E2 and SN2 reactions respectively. Also, E2 reaction above gives alkene Y as single structural isomer which exists as stereoisomers. The SN2 reaction above produced alcohol Z which show stereoisomerism but cannot be resolved into enantiomers.
Q.
The correct statement concerning alcohol (Z) is
Passage II
In an E2 reaction, following one step mechanism is involved.
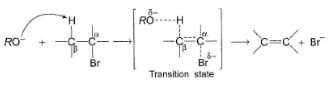
As shown in the above mechanism, a β-proton anti to leaving group is abstracted by the alkoxide base. If a less bulky base is used, β-proton is eliminated giving most substituted, most stable product as the major product. On the otherhand if a bulky base is used, β-proton is abstracted from β-carbon where there is least steric hindrance and this gives least substituted, although least stable, alkene as the major product.
Q.
What is the major product in the following elimination reaction?
Passage II
In an E2 reaction, following one step mechanism is involved.

As shown in the above mechanism, a β-proton anti to leaving group is abstracted by the alkoxide base. If a less bulky base is used, β-proton is eliminated giving most substituted, most stable product as the major product. On the otherhand if a bulky base is used, β-proton is abstracted from β-carbon where there is least steric hindrance and this gives least substituted, although least stable, alkene as the major product.
Q.
In the following reaction, how many elimination products would be formed in principle by E2 mechanism?
Passage II
In an E2 reaction, following one step mechanism is involved.

As shown in the above mechanism, a β-proton anti to leaving group is abstracted by the alkoxide base. If a less bulky base is used, β-proton is eliminated giving most substituted, most stable product as the major product. On the otherhand if a bulky base is used, β-proton is abstracted from β-carbon where there is least steric hindrance and this gives least substituted, although least stable, alkene as the major product.
Q.
What is the major elimination product in the following reaction?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 22-25) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from Ot oQ (both inclusive).
Q.
If trans-3-methylchlorocyclopentane is treated with KOH solution, both SN2 and E2 occur simultaneously. How many total substitution and elimination products are formed in principle?
How many different alkenes would be formed in the following reaction?
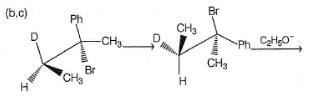
How many different isomers of an alkyl bromide, upon treatment with C2H5ONa in C2H5OH can give 3-methyl-2-hexene as one of the elimination product by E2 mechanism?
An alkene X has molecular formula C11H24. X on free radical chlorination gives three monochloro alkanes derivatives P, Q and R as positional isomers. Only Q is resolvable into enantiomers. P does not undergo E2 elimination reaction with ethanolic KOH solution while Q and R both give the same alkene with ethanolic KOH which is capable of showing geometrical isomerism. How many carbon atoms are present in the parent chain of X?