Test: Reaction of Alcohols - II - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction of Alcohols - II
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (O. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
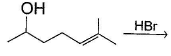
Arrange the following alcohols in the increasing order of reactivity with HBr.
I. benzyl alcohol
II. p-methyl benzyl alcohol
III. p-nitrobenzyl alcohol
IV. p-chlorobenzyl alcohol
I. benzyl alcohol
II. p-methyl benzyl alcohol
III. p-nitrobenzyl alcohol
IV. p-chlorobenzyl alcohol
Which is the most appropriate reagent for the following oxidation reaction?
CH3 —CH = CH — CH2OH → CH3 —CH =CH — COOH
What is the major product of the following reaction ?
Which of the following is true statement regarding reaction of c/s and trans 2-hexene with CH3OH/H+ ?
The major product formed in the following reaction is
The relative rate of reaction of the following with H2SO4
What is the major product of the following reaction?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (0 . Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
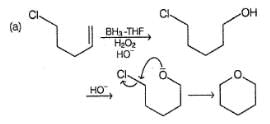
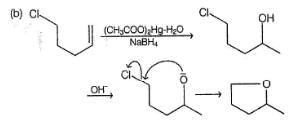
What is/are the expected product(s) in the following reaction?
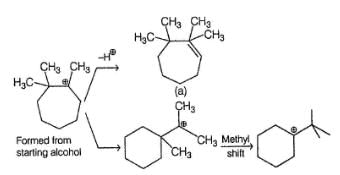
What is/are the possible dehydration product(s) in the following reaction?
What is/are the possible dehydration product(s) in the following reaction?
In which of the following reaction(s), reactant and product(s) are correctly matched ?
In the following dehydration reaction, expected product(s) is/are
Upon treatment with bromine water, allyl bromide gives chiefly primary alcohol BrCH2CHBrCH2OH. What are the expected primary alcohols in the following reaction ?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-19) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Five questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
An unknown organic compound A is determined to have molecular formula C6H12O and passing it through chiral column does not separate it into enantiomers. A does not react with Br2 nor with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4. Heating A with concentrated H2SO4 gives product B (C6H10) which can be separated into enantiomers. Ozonolysis of a single enantiomer of B produces C, an optically active keto-aldehyde of formula C6H10O2 which gives positive iodoform test.
Q.
Structure of B that satisfy the above criteria is
Passage I
An unknown organic compound A is determined to have molecular formula C6H12O and passing it through chiral column does not separate it into enantiomers. A does not react with Br2 nor with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4. Heating A with concentrated H2SO4 gives product B (C6H10) which can be separated into enantiomers. Ozonolysis of a single enantiomer of B produces C, an optically active keto-aldehyde of formula C6H10O2 which gives positive iodoform test.
Q.
The correct statement regarding C is
Passage I
An unknown organic compound A is determined to have molecular formula C6H12O and passing it through chiral column does not separate it into enantiomers. A does not react with Br2 nor with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4. Heating A with concentrated H2SO4 gives product B (C6H10) which can be separated into enantiomers. Ozonolysis of a single enantiomer of B produces C, an optically active keto-aldehyde of formula C6H10O2 which gives positive iodoform test.
Q.
The correct statement regarding the outcome of the following reaction is
Passage II
An organic compound P (C10H18O)w hen treated with Br2(l) gives Q (C10H18OBr4). P on vigorous oxidation gives the following compounds
Q.
What is the structural formula of P?
Passage II
An organic compound P (C10H18O)w hen treated with Br2(l) gives Q (C10H18OBr4). P on vigorous oxidation gives the following compounds
Q.
P on treatment with dilute acid undergo isomerisation to a more stable isomer R. What is the most likely structure of R ?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-23) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
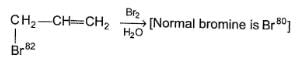
In the reaction given below isotopic exchange occur
Q.
What is the maximum gain in molecular mass observed?
Consider the following dehydration reaction,
Q.
If a pure enantiomer of alcohol is taken, then how many different alkenes are formed?
In the following reaction how many different diols, are formed?
If all carbonyls isomers of molecular mass = 86 u are separately treated with CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis, how many of them will give racemic mixture ?
Arrange the following alcohols in increasing order of acidity:
I. Methanol
II. Ethanol
III. Phenol
IV. Propanol
Which of the following alcohols reacts fastest with HCl in the presence of ZnCl₂ (Lucas Test)?