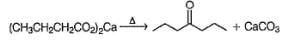Test: Preparation of Aldehydes & Ketones (Morrison & Boyd) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Preparation of Aldehydes & Ketones (Morrison & Boyd)
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
An optically active organic compound has molecular formula C5H12O(X). X on oxidation with CrO3/H2SO4 gives an achiral C5H10O. Hence, X could be
Which of the following reaction will not produce an aldehyde?
Which reagent below cannot reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde?
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is
All of the following reaction gives atleast one ketone as a significant organic product except
All of the following results in the formation of an aldehyde except
Consider the following reaction,
All of the following reagents can bring about the above transformation except
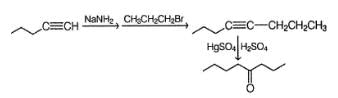
A hydrocarbon X(C7H12) on ozonolysis followed by the treatment with (CH3)2S gives C7H12O2 which gives positive Tollen’s test as well as positive iodoform test. The compoppd below satisfying the criteria of X is
A hydrocarbon X has molecular formula C5H10 X on treatment with B2H6 in H2O2 /NaOH gives an optically active C5H12O which on treatment with CrO3/HCI / pyridine gives C5H10O which is still chiral. Which of the following can be a product of reductive ozonolysis of X?
What is the final major product of the following reaction
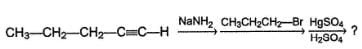
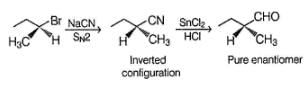
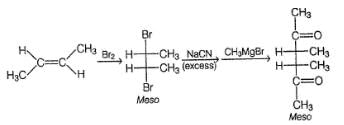
Consider the following reaction,
(A pure enantiomer)
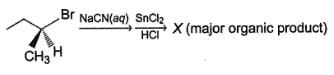
Q.
The incorrect statement regarding X is
Consider the following reaction sequence,
Q.
The correct statement regarding X is
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-17) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (dj, out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
In which of the following reactions, an aldehyde is formed as major product?
In which of the following reactions, ketone is formed as the major organic product?
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The correct statement(s) regarding the above reaction is/are
Consider the reaction mentioned below,
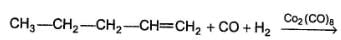
Q.
The expected organic product(s) is/are
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
Reagent(s) that can bring about the above reaction successfully is/are
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,
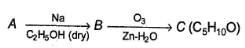 C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
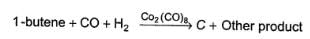
Q.
What is the most likely structure of B?
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,
C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
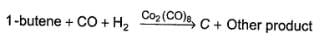
Q.
What is the structure of compound C?
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,
C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
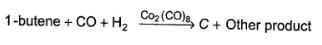
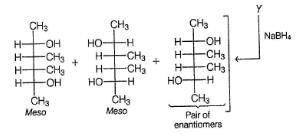
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
How many different alcohols are expected?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
How many different aldehyde isomers exist for C5H10O ?
How many different ketones isomer exist for C6H12O ?
How many different alcohol isomers with molecular formula C5H12O can be oxidised to ketones using K2Cr2O7 - H2SO4?
If all the ketone isomers of C6H10O are reduced independently with NaBH4 , how many of them will produce racemic mixture of alcohols?
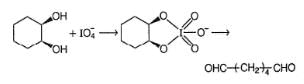
Consider the following reaction,
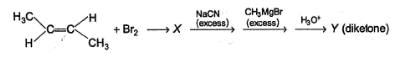
Q.
How many different diols are expected at the end of the above reaction?