CPU 1 - Preparation And General Properties (Carboxylic Acids And Acid Derivatives) - Class 12 MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - CPU 1 - Preparation And General Properties (Carboxylic Acids And Acid Derivatives)
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (cl), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which is the most suitable reagent for the reaction?
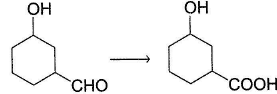
What is the cdfrect about the following reaction?

Predict the major organic product in the following reaction,
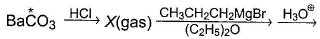
Note Star represent carbon labelled C14
Which reaction given below gives hexanedioic acid in good yield?
Which reaction sequence given below gives 5-methyl hexanoic acid?
What is the major organic product in the reaction given below?
A hydrocarbon X has molar mass of 106. X on vigorous oxidation with hot, alkaline KMnO4 followed by acid hydrolysis gives an organic compound whose neutralisation equivalent is 83. Also X on treatment with Br2/FeCI3 in principal produces three monobromination products. Hence, X could be
In the following synthesis, the major organic product formed is
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which is/are the correct set of reagents that can bring about the following transformation?
Which reagent(s) given below can be used to separate a mixture of butanol and butanoic acid from its ethereal solution?
Which reaction(s) given below gives phthalic acid as the major organic product?
Which reaction sequence given below can convert pentanoic acid into butanoic acid ?
If cis-2-butenedioic acid is treated with Br2(l), the product formed is/are
Which compound (s) given below gives effervescence with NaHCO3?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
An organic compound A(C9H10O3) is optically active. A changes orange colour of CrO3- H2SO4 solution to blue-green. A on vigorous oxidation with hot, concentrated , alkaline KMnO4 gives benzoic acid. Also A on treatment with HBr gives B (C9H9O2Br) with same configuration as that of A.
Q.
What is the structure of A?
An organic compound A(C9H10O3) is optically active. A changes orange colour of CrO3- H2SO4 solution to blue-green. A on vigorous oxidation with hot, concentrated , alkaline KMnO4 gives benzoic acid. Also A on treatment with HBr gives B (C9H9O2Br) with same configuration as that of A.
Q.
Consider the following reaction,
The structure of C is
An organic compound A(C9H10O3) is optically active. A changes orange colour of CrO3- H2SO4 solution to blue-green. A on vigorous oxidation with hot, concentrated , alkaline KMnO4 gives benzoic acid. Also A on treatment with HBr gives B (C9H9O2Br) with same configuration as that of A.
Q.
Which of the following sequence of reaction gives C as the major product?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 18-21) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 fo 9 (both inclusive).
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
How many different tricarboxylic acids are formed?
How many different isomeric methyl cyclohexene, upon treatment with KMnO4/H2SO4/Heat gives dicarboxylic acids?
A hydrocarbon X on treatment with hot, concentrated and alkaline KMnO4, followed by acid work-up gives an acid whose neutralisation equivalent is 83, with same number of carbon atoms as in starting compound X. Also X has a phenyl ring. How many isomers of X exist, all containing a phenyl group?
An unsaturated, acyclic, monobasic carboxylic acid X has neutralisation equivalent of 156. X on treatm ent with KMnO4 /Heat/H2SO4 gives butanoic acid and a dibasic acid Y. How many carbon atoms in Y is /are sp3-hybridised?














