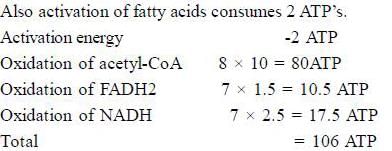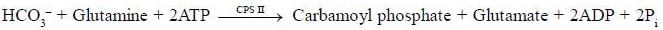Metabolism MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Metabolism MCQ
Which of the following is the committed step of the glycolysis after which glucose cannot enter into Glycogenesis and Pentose Phosphate pathway?
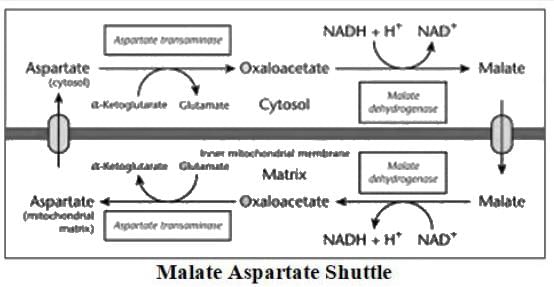
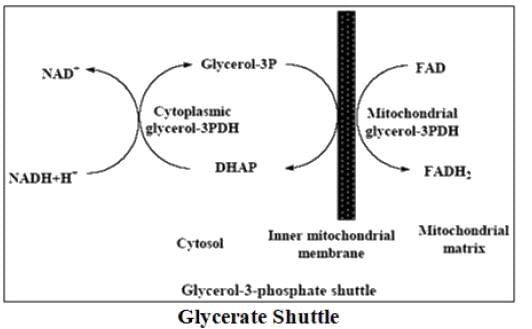
There are two different shuttles for the transport of NADH from cytosol to mitochondrial that decide the net ATP produced from glycolysis. Which of the following shuttles will yield higher ATP per glycolytic pathway
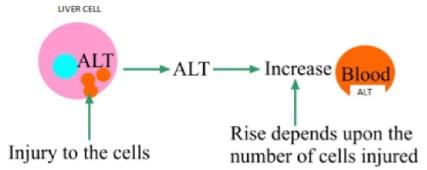
Which of the following enzymes involved in transamination reaction are often used for liver function tests
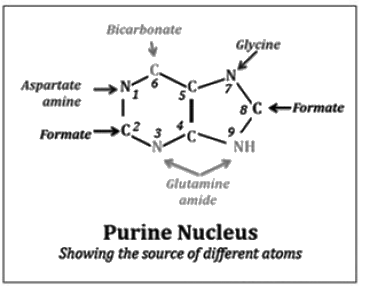
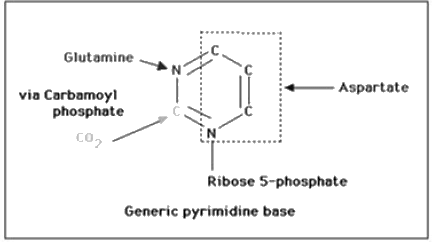
Which of the following amino acid is not needed for nucleotide biosynthesis
The number of ATP generated from oxidation of one molecule of glucose from TCA cycle is
How many ATP are generated from complete oxidation of one molecule of palmitic acid.
Number of ATP generated by beta oxidation of palmitic acid in peroxisomes.
Which of the following is the correct match of the enzyme and the coenzyme used by the enzyme
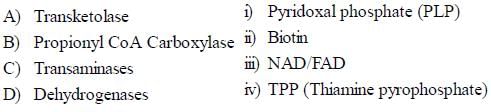
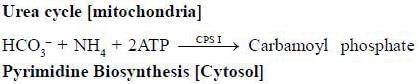
The first step of urea cycle involves the combination of ammonia with bicarbonate at the expense of ATP, resulting in formation of a compound which is also part of nucleotide biosynthesis. The name of this compound is
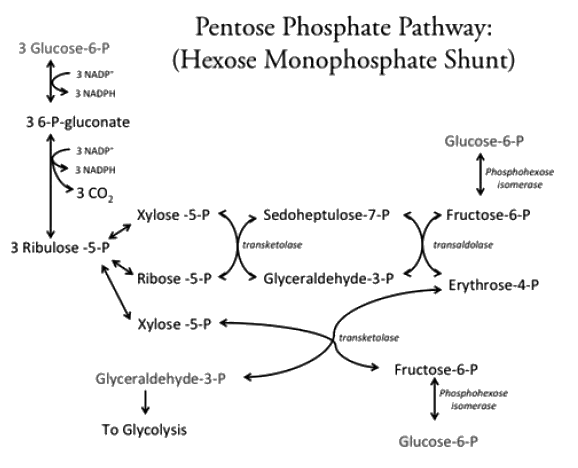
In a radioactive labelling based tracer technique carbon 1 of glucose was labelled and products were evaluated, which of the following statements are true.
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?
The number of ATP needed for the preparatory phase of glycolysis for glycolytic breakdown of 12 glucose molecule is_______________ [Answer in integer]
The number of ATP generated from the complete beta oxidation of C20 fatty acid is _______ [Answer in integer]
The number of ATP generated from complete oxidative phosphorylation of two moles of acetyl CoA molecules is ______________ [Answer in integer]
The net ATP production from fructose 6-phosphate after its conversion into pyruvate in glycolysis during anaerobic conditions is ______________ [Answer in integer]
(Anaerobic conditions prevent the utilization of NADH generated for ATP production)