Test: Network Theorems - 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Network Theorems - 2
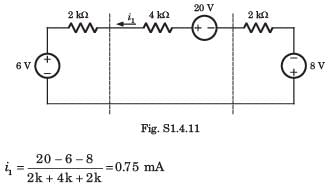
A circuit is given in fig. P.1.4.12–13. Find the Thevenin equivalent as given in question..
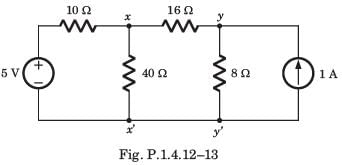
As viewed from terminal y and y' is

As viewed from terminal y and y' is
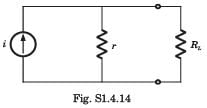
A practical DC current source provide 20 kW to a 50 Ω load and 20 kW to a 200 Ω load. The maximum power, that can drawn from it, is
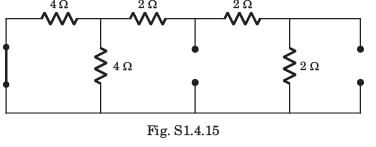
In the circuit of fig. P.1.4.15–16 when R = 0 Ω , the current iR equals 10 A.
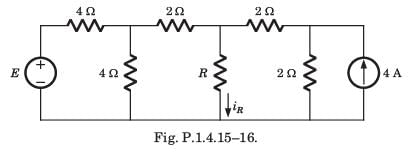
Q. The value of R, for which it absorbs maximum power, is
In the circuit of fig. P.1.4.15–16 when R = 0 Ω , the current iR equals 10 A.
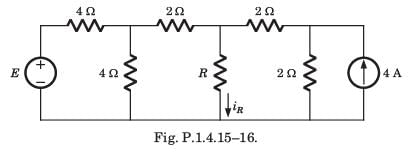
Q. The maximum power will be
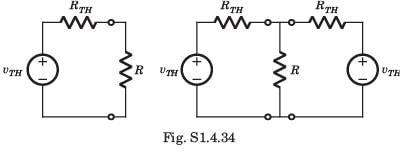
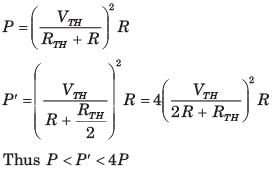
A network N feeds a resistance R as shown in fig.P1.4.34. Let the power consumed by R be P.If an identical network is added as shown in figure, the power consumed by R will be
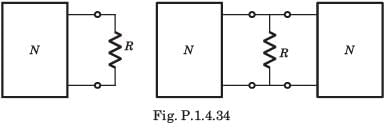
A certain network consists of a large number of ideal linear resistors, one of which is R and two constant ideal source. The power consumed by R is P1 when only the first source is active, and P2 when only the second source is active. If both sources are active simultaneously, then the power consumed by R is
A battery has a short-circuit current of 30 A and an open circuit voltage of 24 V. If the battery is connected to an electric bulb of resistance 2 Ω, the power dissipated by the bulb is
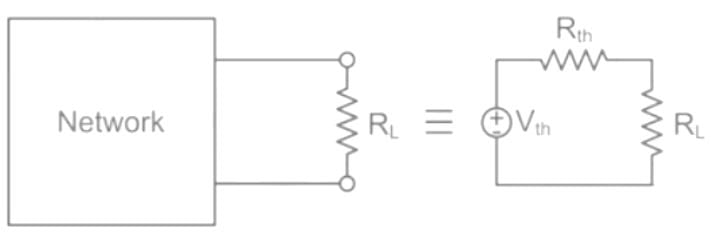
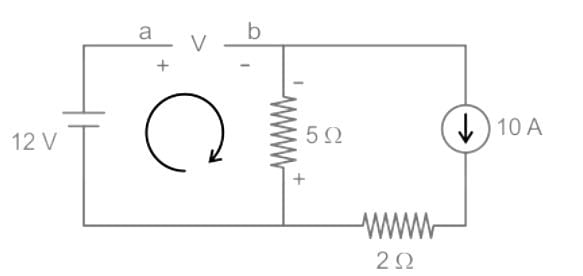
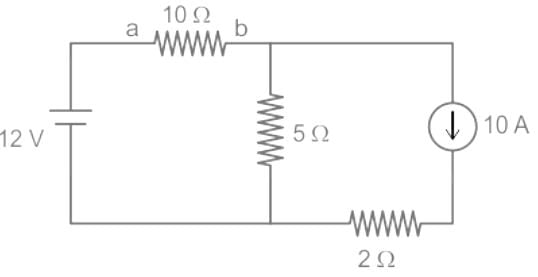
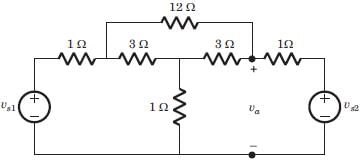
The value of Thevenin's voltage across terminal a - b will be ______.


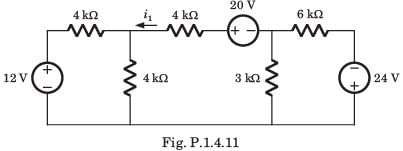
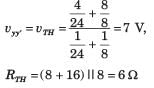

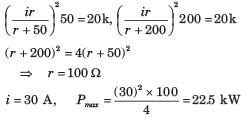
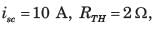
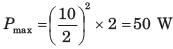
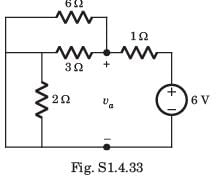
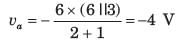
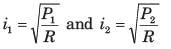
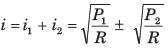
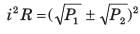
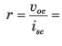 0.8
0.8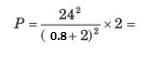 146.93
146.93