Test: Electrolysis & Faraday's Laws - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrolysis & Faraday's Laws
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
During the electrolysis of aqueous Zn(NO3)2 solution
The metal that can not be obtained by electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its salt is
[JEE Main 2014]
When during electrolysis of a solution of AgNO3 ,9650 C of charge pass through the electroplating bath,the mass of silver deposited on the cathode will be
Refining of impure metal is done by electrolysis using impure metal as anode.Select the correct statement about this refining.
W g of Ag is deposited at the cathode of one electrolytic cell due to passage of 1A of current for 1h.Time required for passage of current to deposit W g of Mg by the same value of current is
In the refining of silver by electrolytic method, current of 5A is passed for 2 h using 100 g of impure anode of silver (of 95% purity). Weight of silver anode after electrolysis is
In the electrorefining of metals, impure metal is
In the electrosynthesis,potassium manganate (VII) is converted to manganese(IV) dioxide. By passage of 1F of electrolysis ,one mole of potassium manganate(VII) will form manganese dioxide.
When Al2O3 is electrolysed ,cation and anions are discharged. For a given quantity of electricity,ratio of number of moles of Al and O2 gas is
1 Faraday of electricity is passed through the solution containing 1 mole each of AgNO3, CuSO4, AlCl3 and SiCl4. Elements are discharged at the cathode.Number of moles of Ag, Cu,Al and Si formed will be in the ratio of
During electrolysis of acidified water ,O2 gas is formed at the anode. To produce O2 gas at the anode at the rate of 0.224 cc per second at STP,current passed is
A solution of copper(II) sulphate (VI) is electrolysed between copper electrodes by a currrent of 10.0 A for exactly 9650 s.Which remains unchanged?
A 300 mL solution of NaCl was electrolysed for 60.0 min. If the pH of the final solution was 12.24,average current used is
100 mL of a buffer of 1 M NH3(aq) and 1 M NH4+(aq) are placed in two volatic cells separately.A current of 1.5 A is passed through both cells for 20 min. If electrolysis of water only takes place
2H2O +O2 + 4e- → 4OH- (RHS
2H2O → 4H+. + O2 + 4e- (LHS)
then pH of the
What product are formed during the electrolysis of a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride using an electrolytic cell in which electrodes are separated by a porous pot?
I. Cl2(g)
II. NaOH(aq)
III. H2(g)
IV. NaClO(aq)
V. NaClO3(aq)
Select the correct choice.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Select the correct point(s) of distinction between a volatic cell and electrolysis cell.
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution, two types of reactions can take place at anode :
I. 2Cl- (aq) → Cl2(g) +2e-
II. 2H2O(l)g → O2 (g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e-
Select the correct statement(s) about these.
Select the correct statement(s) about electrolysis of aqueous CuSO4 solution.
Select the correct observation about electrolysis.
Which pair of electrolysis could be distinguished by the products of electrolysis using inert electrodes?
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage I
A constant current of 30 A is passed through an aqueous solution of NaCl for a time of 1.00 h.
Thus NaOH formed due to electrolysis is
Passage I
A constant current of 30 A is passed through an aqueous solution of NaCl for a time of 1.00 h.
Thus Cl2 formed under STP condition is
Passage II
In hydrogen economy fuel-cell,anodic and cathodic reactions are
Anodic
H2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathodic
O2+2H2O + 2e- → 4OH-
67.2 L H2 at STP react in 15 min.Entire current is used for electro deposition of copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. Average current produced in fuel cell is
Passage II
In hydrogen economy fuel-cell,anodic and cathodic reactions are
Anodic
H2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathodic
O2+2H2O + 2e- → 4OH-
67.2 L H2 at STP react in 15 min.Entire current is used for electro deposition of copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. Copper deposited would be
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 6 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Mn+ solution was electrolysed for 75 min by a current of 0.30 A. Mass of the metal M deposited at the cathode was 9.958 g.Mn+ contains 68 protons and 69 neutrons. What is the value of n?
An electrochemical cell was based on the following reaction:
Mn(OH)2(s) + H2O2(aq) → MnO2(s) + 2H2O (e)
During the opeartion of this for 1 min, 0.135 g of MnO2 was produced. What is the average electric current (in ampere ) produced by the cell?
In a fuel cell, following reactions takes place and electricity is produced.
Anodic
H2+2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathodic
O2+2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
If 100.8 L of H2 at STP reacts in 96500 s,what is the average current produced (in ampere)?
How long (in minutes ) a current of 1.56 A has to be passed through a solution of AgNO3 to coat a metal surface of 80 cm2 with a 0.010 mm thick layer? Density of silver is 10.5 g cm-3.
A fully charged battery contains 500 mL of 5.00 M H2SO4. What is the concentration of H2SO4 in the battery after 6.0 A of current is drawn from the battery for 13.40 h?



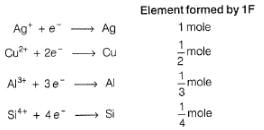
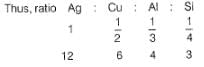
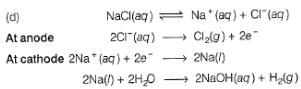
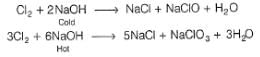
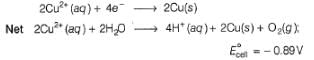 since, E0cell < 0, in electrolysis.
since, E0cell < 0, in electrolysis.















