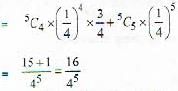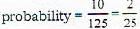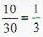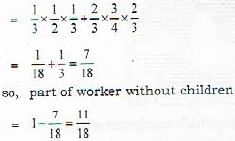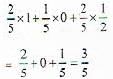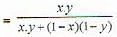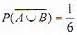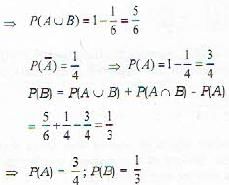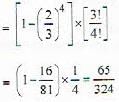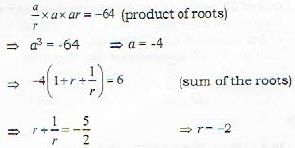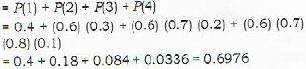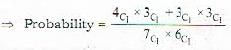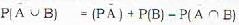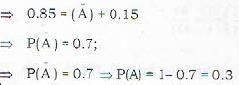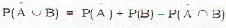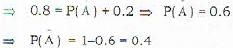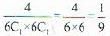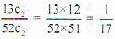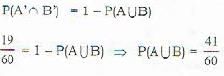Test: Probability and Statistics - 9 - Mathematics MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Probability and Statistics - 9
If a student is likely to choose any of the four choices with equal probability in a multiple-choice examination with five questions then the probability that the student answer at least four questions correctly is
Let 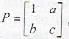 where a, b, c are chosen randomly from the set {1,2,3,4,5}. The probability that P is singular is
where a, b, c are chosen randomly from the set {1,2,3,4,5}. The probability that P is singular is
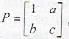 where a, b, c are chosen randomly from the set {1,2,3,4,5}. The probability that P is singular is
where a, b, c are chosen randomly from the set {1,2,3,4,5}. The probability that P is singular isSubway trains on a certain line run every half hour between midnight and six in the morning. Find the probability that a person entering the station at a random time during this period will have to wait at least twenty minutes.
In a certain office, 1/3 of the workers are women, 1 /2 of the women are married and 1 /3 of the married women have children. If 3/4 of the men are married and 2/3 of the married men have children, what part of workers are without children?
A man has 5 coins, two of which are double - headed, one is double - tailed and two are normal. He shuts his eyes, picks a coin at random, and tosses it. The probability that the lower face of the coin is a head is
A and B are independent witnesses in a case. The probability that A speaks the truth is 'x' and that B speaks the truth is ‘y'. If A and B agree on a certain statement, the probability that the statement is true is
Let A and B be two events such that 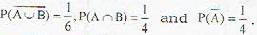 Then events A and B
Then events A and B
The probability that a man who is 85 yrs. old will die before attaining the age of 90 is 1 / 3. A1, A2, A3 and A4 are four persons who are 85 yrs. old. The probability that A1 will die before attaining the age of 90 and will be the first to die is
Find the value of k in the equation x3 -6x2 + kx + 64 = 0, if it is known that the roots of the equation are in geometric progression.
An anti aircraft gun can take a maximum of four shots at an enemy plane moving away from it. The probabilities of hitting the plane at first, second, third and fourth shot are 0.4, 0.3, 0.2 and 0.1 respectively. The probabality that the gun hits the plane then is
A bag contains 4 while and 3 black balls and a second bag contains 3 white and 3 black balls. If a ball is drawn from each of the bags, then the probability that both are of same colour is:
The probability of getting atleast 6 head in 8 trials is:
Bag A contain 10 bulbs in which 3 bulbs are defective. 2 bulbs are drawn. What is the probability of the both bullps being non-defective?
Prob. of getting an odd number or a no. less than 4 in throwing a dice is :
Given A and B are mutually exclusive events. If P(B) = 0.15
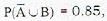 P(A) is equal to
P(A) is equal to
In a pack of 52 cards, the probability of drawing at random such that it is diamond or card king is:
Given A and Bare mutually exclusive events.if: P(A ∪ B) = 0.8, P(B) = 0.2 then P(A) is equal to
Two dice are thrown once the probability of getting a sum 9 is given by :
In a pack of 52 cards. Two cards are drawn at random. The probability that it being club card is:
If P(A∩B) is equal to 19/60 then P(A∪B) is equal to