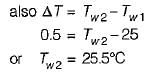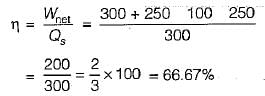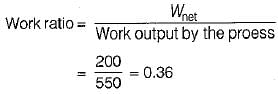Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 1
The first law of thermodynamics is the law of
In a cyclic process, heat transfer are +15.7 kJ, -26.2 kJ, -4.86 kJ and +31.5 kJ. What is the network for this cyclic process?
A stationary mass of gas is compressed without friction from an initial state of 0.3 m3 and 0.1 MPa to a final state of 0.15 m3 and 0.1 MPa, the pressure remaining constant during the process. There is a transfer of 40 kJ of heat from the gas during the process. What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
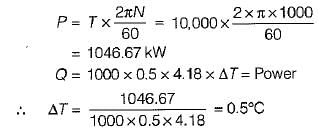
An engine is tested by means of a water brake at 1000 rpm. The measured torque-of the engine is 10000 Nm and the water consumption of the brake is 0.5 m3/s, its inlet temperature being 25°C. Assuming that the whole of the engine power is ultimately transferred into heat which is absorbed by the cooling water, what is the water temperature at exit?
What reaction takes place during photosynthesis?
What is the temperature rise after 5 minutes in the below volume?
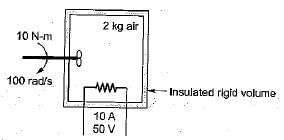
Energy is added to 5 kg of air with a paddle wheel so that ΔT = 100°C while P = const. in an insulated container. The paddle-wheel work is
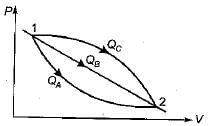
An ideal gas of mass m at state 1 expands to state 2 via three paths. If QA, QB and Qc represent the heat absorbed by the gas along three paths, then
The values of heat and work transfer for the flow processes of a thermodynamic cycle are given below:
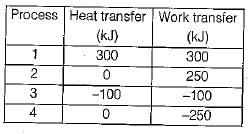
The thermal efficiency and work ratio for the cycle will be respectively




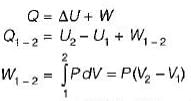
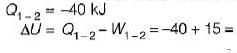 -25Kj
-25Kj