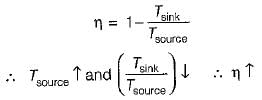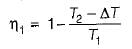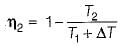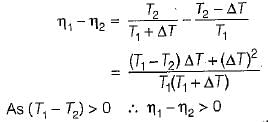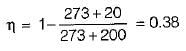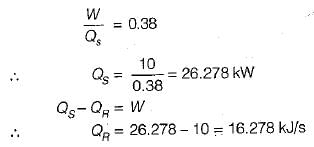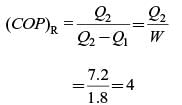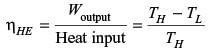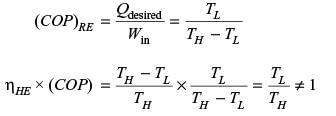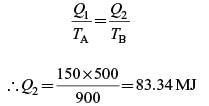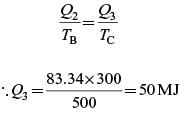Test: Second Law of Thermodynamics - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Second Law of Thermodynamics - 1
Select the Kelvin-Plank statement of the second law:
According to the Clausius statement of the second law:
1. heat flows from cold surface to hot surface, unaided.
2. heat flows from hot surface to cold surface, unaided.
3. heat can flow from cold surface to hot surface with the aid of external work
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. heat flows from cold surface to hot surface, unaided.
2. heat flows from hot surface to cold surface, unaided.
3. heat can flow from cold surface to hot surface with the aid of external work
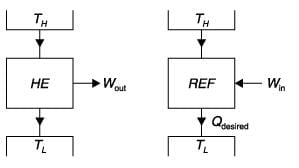
If a heat engine attains 100% thermal efficiency, it violates
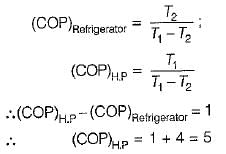
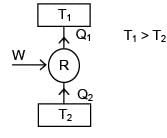
A refrigerator and a heat pump operate between the same temperature limits. If the COP of the refrigerator is 4, the COP of the heat pump would be
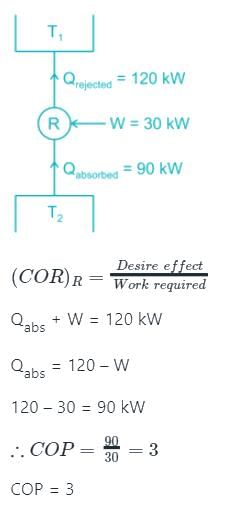
A condenser of a refrigeration system rejects heat at a rate of 120 kW, while its compressor consumes a power of 30 kW. The coefficient of performance of the system would be
If the temperature of the source is increased keeping sink temperature fixed, the efficiency of the Carnot engine
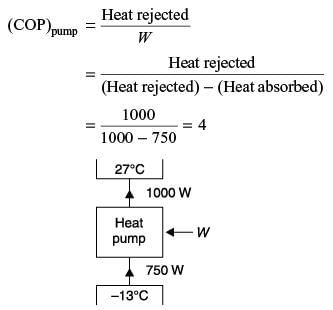
An industrial heat pump operates between the temperatures of 27°C and –13°C. The rates of heat addition and heat rejection are 750 W and 1000 W, respectively. The COP for the heat pump is
The more effective way of increasing the efficiency of a Carnot engine is to
A Carnot engine operates between reservoirs at 20°C and 200°C. If 10 kW of power is produced, the rejected heat rate is nearest
An inventor invents a thermal engine that operates between ocean layers at 27°C and 10°C. It produces 10 kW and discharges 9900 kJ/min of heat. Such an enigne is
If the time taken by a system to execute a process through a finite gradient is infinitely large, the process
“Heat cannot be transported from a system at low temperature to another system at high temperature without the aid of external agency”. This statement of second law is attributed to
The heat removal rate from a refrigerated space and the power input to the compressor are 7.2 kW and 1.8 kW, respectively. The coefficient of performance (COP) of the refrigerator is .
Any thermodynamic cycle operating between two temperature limits is reversible if the product of the efficiency when operating as a heat engine and the COP when operating as a refrigerator is equal to 1.
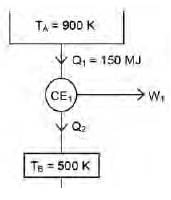
A Carnot engine (CE-1) works between two temperature reservoirs A and B, where TA = 900 K and TB = 500 K. A second Carnot engine (CE-2) works between temperature reservoirs B and C, where TC = 300 K. In each cycle CE-1 and CE-2, all the heat rejected by CE-1 to reservoir B is used by CE-2. For one cycle of operation, if the net Q absorbed by CE-1 from reservoir A is 150 MJ, the net heat rejected to reservoir C by CE-2 (in MJ) is .