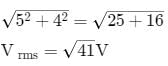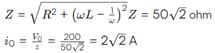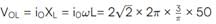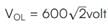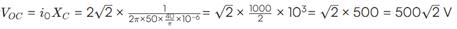Test: Alternating Current - 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Alternating Current - 3
In an a.c. circuit voltage V and current i are given by V = 100 sin 100 t volts, i = 100 sin (100t + p/3) mA. The power dissipated in the circuit is :
The potential difference V and current i flowing through an a.c. circuit are given by V = 5 cos wt volt, i = 2 sin wt amp. the power dissipated in the circuit.
An a.c. circuit consists of an inductor of inductances 0.5 H and a capacitor of capacitance 8 mF in series. The current in the circuit is maximum when the angular frequency of an a.c. source is
The rms value of an AC of 50 Hz is 10 amp. The time taken by an alternating current in reaching from zero to maximum value and the peak value will be ;
A voltage of peak value 283 V varying frequency is applied to a series L-C-R combination in which R = 3W; L = 25 mH and C = 400 mF. Then, the frequency (in Hz) of the source at which maximum power is dissipated in the above, is
The power factor of the circuit is 1/. The capacitance of the circuit is equal to
An ac-circuit having supply voltage E consists of a resistor of resistance 3W and an inductor of reactance 4W as shown in the figure. The voltage across the inductor at t = p/w is
When 100 V DC is applied across a solenoid a current of 1A flows in it. When 100 V AC is applied across the same coil, the current drops to 0.5 A. If the frequency of the AC source is 50 Hz, the impedance and inductance of the solenoid are :
An inductive circuit contains a resistance of 10 ohm and an inductance of 2.0 henry. If an ac voltage of 120 volt and frequency of 60 Hz is applied to this circuit, the current in the circuit would be nearly :
In the circuit shown if the emf of source at an instant is 5V, the potential difference across capacitor at the same instant is 4V. The potential difference across R at that instant may be
Let f = 50 Hz, and C = 100 mF in an AC circuit containing a capacitor only. If the peak value of the current in the circuit is 1.57 A at t = 0. The expression for the instantaneous voltage across the capacitor will be
In a series CR circuit shown in figure, the applied voltage is 10 V and the voltage across capacitor is found to be 8V. Then the voltage across R, and the phase difference between current and the applied voltage will respectively be
The phase difference between current and voltage in an AC circuit is p/4 radian. If the frequency of AC is 50 Hz, then the phase difference is equivalent to the time difference :
The given figure represents the phasor diagram of a series LCR circuit connected to an ac source. At the instant t' when the source voltage is given by V = V0coswt, the current in the circuit will be
Power factor of an L-R series circuit is 0.6 and that of a C_R series circuit is 0.5. If the element (L, C, and R) of the two circuits are joined in series the power factor of this circuit is found to be 1. The ratio of the resistance in the L-R circuit to the resistance in the C-R circuit is
The direct current which Would give the same heating effect in an equal constant resistance as the current shown in figure, i.e. the r.m.s. current, is
The effective value of current i = 2 sin 100p t + 2 sin (100pt + 30º) is
A student in a lab took a coil and connected it to a 12 V DC source. He measures the steady state current in the circuit to be 4A. He then replaced the 12 V DC source by a 12 V, (w = 50 rad/s) AC source and observes that the reading in the AC ammeter is 2.4 A. He then decides to connect a 2500 mF capacitor in series with the coil and calculate the average power developed in the circuit. Further he also decides to study the variation in current in the circuit (with the capacitor and the battery in series).
Based on the readings taken by the student answer the following questions.
The value of resistance of the coil calculated by the student is
A student in a lab took a coil and connected it to a 12 V DC source. He measures the steady state current in the circuit to be 4A. He then replaced the 12 V DC source by a 12 V, (w = 50 rad/s) AC source and observes that the reading in the AC ammeter is 2.4 A. He then decides to connect a 2500 mF capacitor in series with the coil and calculate the average power developed in the circuit. Further he also decides to study the variation in current in the circuit (with the capacitor and the battery in series).
Based on the readings taken by the student answer the following questions.
The power developed in the circuit when the capacitor of 2500 mF is connected in series with the coil is
A student in a lab took a coil and connected it to a 12 V DC source. He measures the steady state current in the circuit to be 4A. He then replaced the 12 V DC source by a 12 V, (w = 50 rad/s) AC source and observes that the reading in the AC ammeter is 2.4 A. He then decides to connect a 2500 mF capacitor in series with the coil and calculate the average power developed in the circuit. Further he also decides to study the variation in current in the circuit (with the capacitor and the battery in series).
Based on the readings taken by the student answer the following questions.
Which of the following graph roughly matches the variations of current in the circuit (with the coil and capacitor connected in the series) when the angular frequency is decreased from 50 rad/s to 25 rad/s ?
If a direct current of value 'a' ampere is superimposed on an alternating current I = b sin wt flowing through a wire, what is the effective (rms) value of the resulting current in the circuit ?
Find the average for the saw-tooth voltage of peak value V0 from t = 0 to t = 2T as shown in figure.
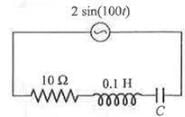
A circuit has a coil of resistance 50 ohms and inductance henry. It is connected in series with a condenser of
m F and AC supply voltage of 200 V and 50 cycles/sec. Calculate
(i) the impedance of the circuit. (ii) the p.d. across inductance coil and condenser.
A series circuit consists of a resistance, inductance and capacitance. The applied voltage and the current at any instant are given by E = 141.4 cos (5000 t _ 10°) and I = 5 cos (5000 t _ 370°) The inductance is 0.01 henry. Calculate the value of capacitance and resistance.
A circuit takes A current of 3 a at a power factor of 0.6 lagging when connected to a 115 V _ 50 Hz supply. Another circuit takes a current of 5A at a power factor of 0.07 leading when connected to the same supply. If the two circuits are connected in series across a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. Calculate
(a) the current (b) the power consumed and (c) the power factor.