Test: Introduction & IP Addressing- 1 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Introduction & IP Addressing- 1
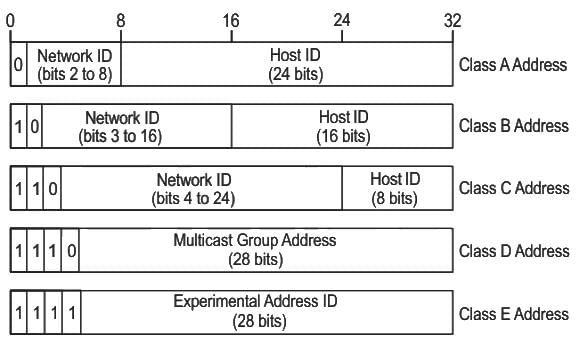
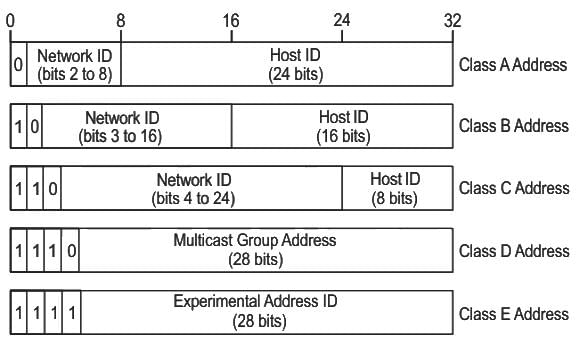
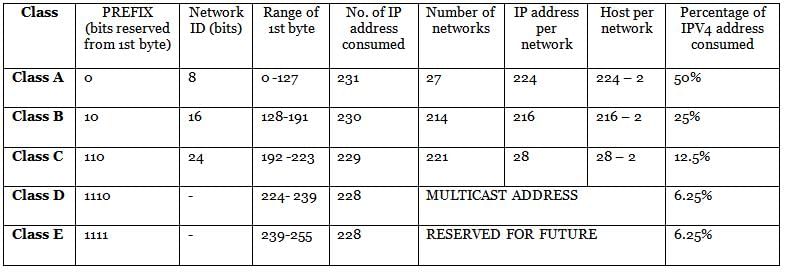
Class ‘C’ IP addresses use ______ bits for Network ID.
You are working with a network that is 172.16.0.0 and would like to support 600 hosts per subnet. What subnet mask should you use?
An IPv4 address is a __________ address, which is categorised into different IP classes.
Match List - I with List - II.
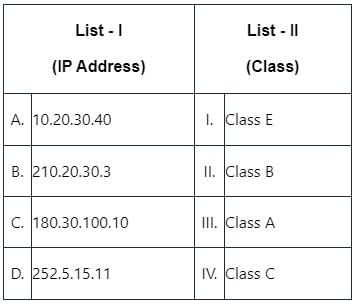
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The IP address _______ is used by hosts when they are being booted.
In the IPv4 addressing format, the number of networks allowed under Class C addresses is
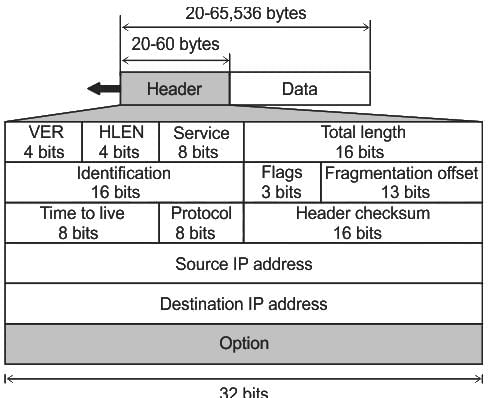
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?
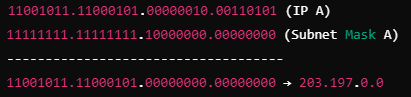
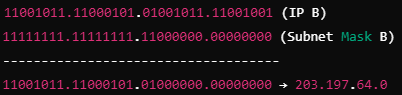
Two computers A and B are configured as follows: A has IP address 203.197.2.53 and subnet mask 255.255.128.0, B has IP address 203.197.75.201 and subnet mask 255.255.192.0. What one of the following statement is true?
What flavour of Network Address Translation can be used to have one IP address allow many users to connect to the global internet?