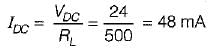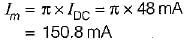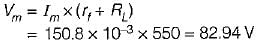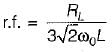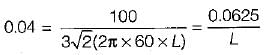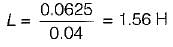Test: Diode Circuits - 1 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Diode Circuits - 1
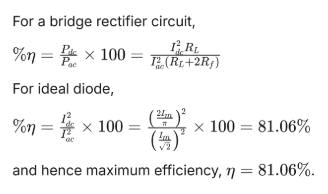
The theoretical maximum efficiency of a bridge rectifier circuit is
What is the primary reason a full-wave rectifier without a filter has a lower ripple factor compared to a half-wave rectifier?
Assertion (A): The ripple voltage in a full-wave rectifier’s output can be minimized by adding a filter capacitor across the load.
Reason (R): The capacitor stores charge during voltage peaks and releases it during troughs, smoothing the output voltage.
Reason (R): The capacitor stores charge during voltage peaks and releases it during troughs, smoothing the output voltage.
A half wave rectifier is used to supply 24 V DC to a resistive load of 500 Ω and the diode has a forward resistance of 50 Ω. What is the maximum value of the AC voltage required at the input?
What is the value of inductance to be used in the inductor filter connected to a full-wave rectifier operation at 60 Hz to provide a DC output with 4% ripple for a 100 Ω load?
Diodes are used to clip voltages in circuits because they act as
When a capacitor is connected across the output terminals of a half or full-wave rectifier, the output voltage
The equivalent DC output voltage of a full-wave rectifier is ____ the equivalent DC output voltage of a half-wave rectifier.
Assertion (A): A high value of resistor is connected across the diode in a clamper circuit for better performance.
Reason (R): If this resistor is not present, the circuit will respond to sudden decrease in the magnitude of the input pulse train, but the response to sudden increase in the amplitude will cause improper response.
Assertion (A): Bridge arrangement is preferred over centre-tapped transformer arrangement for full-wave rectification.
Reason (R): The bridge arrangement improves the filtering action.