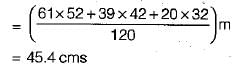Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Tests > Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test Description
9 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus.The Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology below.
Solutions of Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology questions in English are available as part of our course for Civil Engineering (CE) & Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology solutions in
Hindi for Civil Engineering (CE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology | 9 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Civil Engineering (CE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 1
The % of earth covered by oceans is about
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 1
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 2
The percentage of total quantity of water in the world that is saline is about
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 2
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 3
The percentage of total quantity of fresh water in the world available in the liquid form is about.
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 3
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 4
A catchment has an area of 150 ha and a runoff/ rainfall ratio of 0.40. If due to a 10 cm rainfall over the catchment a stream flow at the catchment outlet lasts for 10 hours, the average stream flow in the period is
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 4
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 5
A catchment of area 120 km2 has three distinct zones as below

The annual runoff from the catchment, in cms, is
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 5
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 6
If the average annual rainfall and evaporation over land masses and oceans of the earth are considered it would be found that
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 6
Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 7
In the hydrological cycle the average residence time of water in the global
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology - Question 9
Information about Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Introduction to Engineering Hydrology, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF