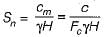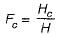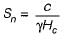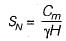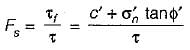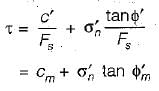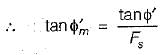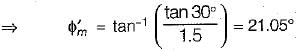Test: Stability of Earth Slopes - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stability of Earth Slopes
A cohesionless soil having an angle of shearing resistant of ϕ, is standing at a slope angle of i. The factor of safety of the slope is:
A finite slope of cohesion less soil is safe so long as
In the friction circle method the radius of the friction circle is given by
Taylor's stability number is equal to
where c = unit cohesion, Fc = factor of safety with respect to cohesion, γ = unit weight of soil, Hc = critical height, H = actual height
If the unit weight of soil is 20 kN/m3 cohesion is 15 kN/m2, factor of safety is 1.5 and the stability number is 0.05, the safe maximum height of the slope is
An infinite soil slope with an inclination of 35° is subjected to seepage parallel to its surface. The soil has c' = 100 kN/m2 and ϕ = 30°. Using the concept of mobilized cohesion and friction, at a factor of safety of 1.5 with respect to shear strength, the mobilized friction angle is
List-I given below gives the possible types of failure for a finite soil slope and List-II gives the reasons for these different types of failure. Match the items in List-I with the items in List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Base failure
B. Face failure
C. Toe failure
List-II
1. Soils above and below the toe have same strength
2. Soil above the toe is comparatively weaker
3. Soil above the toe is comparatively stronger
Taylor’s stability number curves are used for the analysis of stability of slopes. The angle of shearing resistance used in the chart is the:
An excavation was made at a slope angle of 54° in homogeneous clay. When the depth of excavation reached 8m, a slip occurred. The slip surface was likely to have passed through a point:
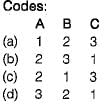
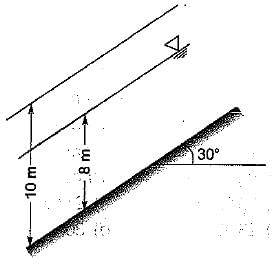
The factor of safety of an infinite soil slope shown in the figure having the properties c = 0, ϕ = 35°, γdry = 16kN/m3 and γsat = 20 kN/m3 is approximately equal to


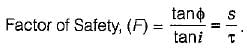

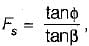 from which
from which