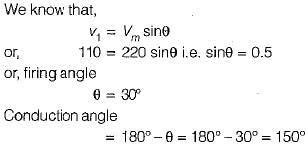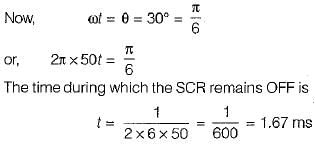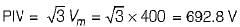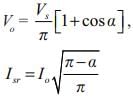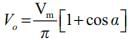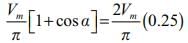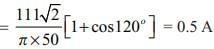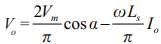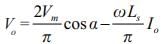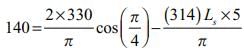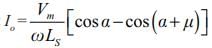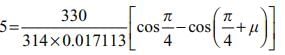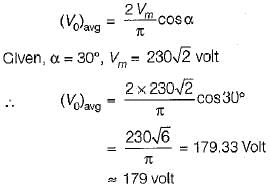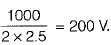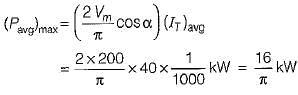Test: Phase Controlled Rectifiers - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Phase Controlled Rectifiers - 1
In an SCR half wave rectifier, the forward breakdown voltage of SCR is 110 V for a gate current of 1 mA. If a 50 Hz sinusoidal voltage of 220 V peak is applied, the time during which SCR remains OFF would be equal to (assume load resistance is 100 Ω and the holding current to be zero)
When an SCR full wave rectifier is connected across a sinusoidal voltage of 400 sin 314t, the RMS value of the current flowing through the device is 20 A. The power rating of the SCR is
A single phase semi converter feed RLE load such that load current is constant for a firing angle of 90°. The input power factor will be
A single phase semi converter is operated from a 50Hz, 111V ac source. If a resistive load of 50 Ω is connected at the dc terminals of converter and the averageoutput voltage is 25% of the maximum possible average output voltage, the average load current will be?
A single phase full converter is connected to an AC supply of 330 sin 314t volts. It operates at firing angle 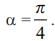 The load current is maintained constant at 5A and load voltage is 140V. The angle of overlap due to effect of source will be
The load current is maintained constant at 5A and load voltage is 140V. The angle of overlap due to effect of source will be
A single-phase full converter is connected across 230 V ac. Its average output voltage when firing angle is 30° is approximately equal to
SCRs with peak forward rating of 1 kV and average on-state current rating of 40 A is used in single-phase mid-point converter. If the factor of safety is 2.5, then the power that this converter can handle is
The main advantages of the dual converter with circulating current operation is/are
1. the efficiency and power factor are more.
2. it has faster operation than dual converter without circulating current.
3. the thyristors are rated for lower current.
Choose the correct code from the following
The average value of voltage of a single-phase ac voltage converter with resistive load is (α is the firing angle).