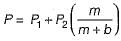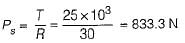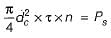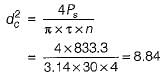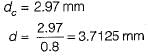Test: Threaded Joints & Power Screws - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Threaded Joints & Power Screws - 2
The resultant axial load on a bolt depends upon
1. external load applied
2. initial tension due to tightening of bolt
3. relative elastic yielding of the bolt and connected member
Which of the above statements are correct?
1. external load applied
2. initial tension due to tightening of bolt
3. relative elastic yielding of the bolt and connected member
Which of the above statements are correct?
A bolt is to be used for making a fluid tight joint steam engine cover plates. Which of the following relation is used for initial tension (in N) in the bolt?
where d is the nominal bolt diameter in mm.
where d is the nominal bolt diameter in mm.
The most important dimension in the design of nut is its
Which of the following locking devices has the widest application in automobile industry?
Two shafts are connected by means of a flange coupling to transmit torque of 25 N-m. The flanges of the coupling are fastened by four bolts of the same material at a radius of 30 mm. What is the size of bolts if the allowable shear stress for the botl material is 30 MPa?
For bolts of uniform strength, the shank diameter is made equal to
How can shock absorbing capacity of a bolt be increased