Test: Timber - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Timber - 2
Fibre saturation point of timber is the moisture content in % when
Consider the following statements:
Seasoning of timber results'in
1. increased strength
2. increased durability
3. reduced resilience
Which of these statements are correct?
Seasoning of timber results'in
1. increased strength
2. increased durability
3. reduced resilience
Consider the following statements:
Among the more common varieties of timber, namely, sal, mango and deodar,
1. sal is the strongest
2. mango is the least durable
3. deodar is the lightest
Which of these statements are correct?
Which of the following pairs regarding the defects in timber are correctly matched
1. Upsets : Due to overmatuarity and unventilated storage of wood
2. Foxiness : Due to crushing of fibres running transversely
3. Star shakes : Radial splits widest at the circumference and diminishing towards the centre
4. Heart shakes : Cracks widest at the centre and diminishing towards the outer circumference
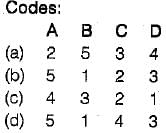
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Consider the following methods of preservation of timber
1. Dipping
2. Brushing or spraying
3. Pressure impregnation
The correct sequence in decreasing order of the effectiveness of these methods of preservation is
Cracks in a tree may develop due to
1. storm
2. drying of core
3. frost
Which of these statements is/are correct?
The purpose of seasoning of wood is to
1. reduce the voids
2. remove the curves
3. reduce the moisture content
4. change the direction of grains
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes give below the lists:
List-I
A. The innermost part or core of the stem of a tree
B. The vascular tissue which encloses the pitch
C. A cellular tissue and woody fibre arranged in distinct concentric circle
D. The thin layer below the bark not converted into sap wood as yet
List-ll
1. Transverse Septa (Medullary rays)
2. Annual rings
3. The cambium layer
4. The outermost cover or skin of stem
5. Medulla (Pith)
As a construction material, plywood is preferred to thin planks of timber because of














