Test: Methods of Indeterminate Analysis -2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Methods of Indeterminate Analysis -2
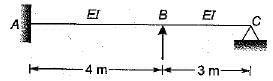
A horizontal fixed beam AB of span 6 m has uniform flexural rigidity of 4200 kN m2. During loading, the support B sinks downwards by 25 mm. The moment induced at the end A is
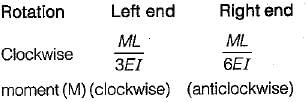
A uniform simply supported beam is subjected to a clockwise moment M at the left end. What is the moment required at the right end so that rotation of the right end is zero?
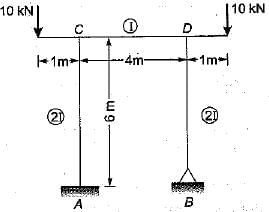
The possible direction of sway of the rigid frame shown in figure

Four identical beams AE, BE, CE and DEhave been rigidly jointed at E The point O slip and rotates along with member firmly fixed at E.
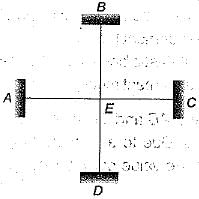
Which one among the following is correct?
Match List-I (Method) with List-lI (Factor) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I
A. Moment distribution method
B. Slope deflection method
C. Kani’s method
D. Force method

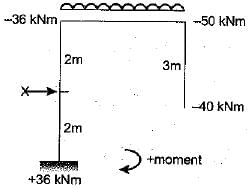
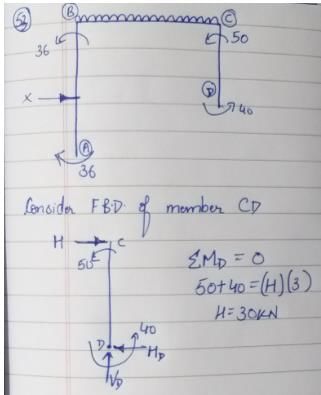
Final moment values got through the analysis of a portal frame have been shown in the figure. What is the value of X?
The figure given above shows a rigid frame. If D . is lateral translation of the joints, slope deflection equation for the member BA be written as:
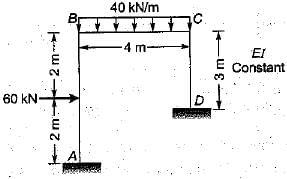
What are the distribution factors at joint 6 for the members BA and BC respectively, in the figure?
Which one of the following statements is correct? The principle of superposition is applicable to
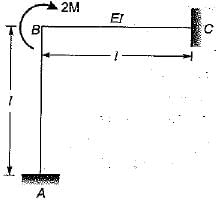
Members AB and BC in the figure shown are identical. Due to a moment 2M applied at B, what is the value of axial force in the member AB?


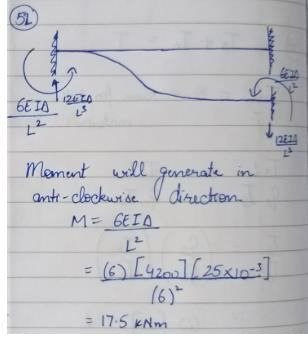



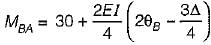
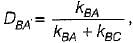

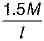 but compressive.
but compressive.










