Physical Properties Of Metals -2 - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Physical Properties Of Metals -2
What happens when calcium is treated with water ?
(i) It does not react with water.
(ii) It reacts violently with water.
(iii) It reacts less violently with water.
(iv) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium.
(i) It does not react with water.
(ii) It reacts violently with water.
(iii) It reacts less violently with water.
(iv) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium.
Which one of the following figures correctly describes the process of electrolytic refining ?
The ability of the metals to be drawn into thin wires is known as
Which of the following can undergo a chemical reaction ?
Which of the following metals exist in their native state in nature ?
(i) Cu
(ii) Au
(iii) Zn
(iv) Ag
Although metals form basic oxides, which of the following metals form an amphoteric oxide ?
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating with a thin layer of
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X —2, 8; Y — 2,8,7 and Z — 2, 8, 2. Which of the following is correct ?
Stainless steel is very useful material for our life. In stainless steel, iron is mixed with
Reaction between X and Y, forms compound Z. X loses electron and Y gains electron. Which of the following properties is not shown by Z ?
Generally, non-metals are not lustrous. Which of the following non-metal is lustrous ?
Which among the following alloys contain mercury as one of its constituents ?
Which one of the following four metals would be displaced from the solution of its salts by other three metals ?
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
Which of the following are not ionic compounds ?
(i) KCl
(ii) HCl
(iii) CCl4
(iv) NaCl
An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept open in air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element from the following
Electrical wires have a coating of an insulating material. The material, generally used is
An electrolytic cell consists of
(i) positively charged cathode
(ii) negatively charged anode
(iii) positively charged anode
(iv) negatively charged cathode
Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas. Which of the following acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg) ?
2 mL each of concentrated HCl, HNO3 and a mixture of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO3 in the ratio of 3 :1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metal got dissolved in test tube C respectively. The metal could be


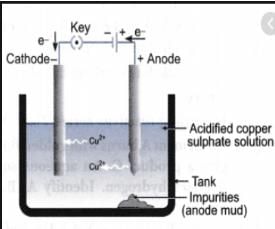 Electrolytic refining is the process of refining impure metals by using electricity. In this process, impure metal is made the anode and a strip of pure metal is made the cathode. A solution of a soluble salt of the same metal is taken as the electrolyte. When an electric current is passed, metal ions from the electrolyte are deposited at the cathode as pure metal and the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte in the form of ions. The impurities present in the impure metal gets collected below the anode. This is known as anode mud.
Electrolytic refining is the process of refining impure metals by using electricity. In this process, impure metal is made the anode and a strip of pure metal is made the cathode. A solution of a soluble salt of the same metal is taken as the electrolyte. When an electric current is passed, metal ions from the electrolyte are deposited at the cathode as pure metal and the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte in the form of ions. The impurities present in the impure metal gets collected below the anode. This is known as anode mud.











