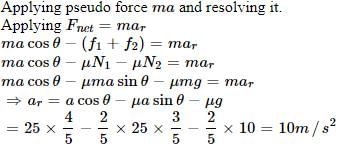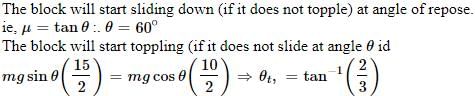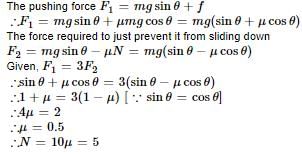JEE Previous Year Questions: Laws of Motion- 2 - JEE MCQ
9 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Previous Year Questions: Laws of Motion- 2
Mass of the object is quantitative measure of its inertia stated law is newton's
Two blocks A and B masses 2m and m, respectively, are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of A and B, immediately after the string is cut, are respectively.
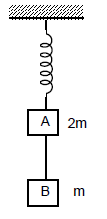
[JEE 2006]
A circular disc with a groove along its diameter is placed horizontally. A block of mass 1 kg is placed as shown. The co-efficient of friction between the block and all surfaces of groove in contact is m = 2/5. The disc has an acceleration of 25 m/s2. Find the acceleration of the block with respect to disc.
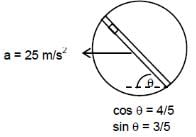
[JEE 2006]

STATEMENT-1 A cloth Covers a table. Some dishes are kept on it. The cloth can be pulled out without dislodging the dishes from the table
because
STATEMENT-2 For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Statement-1 It is easier to pull a heavy object than to push it on a level ground.
and
Statement-2 The magnitude of frictional force depends on the nature of the two surfaces in contact .
[ JEE 2008]
A block of base 10 cm × 10 cm and height 15 cm is kept on an inclined plane. The coefficient of friction between them is . The inclination q of this inclined plane from the horizontal plane is gradually increased from 0º. Then [jee 2009]
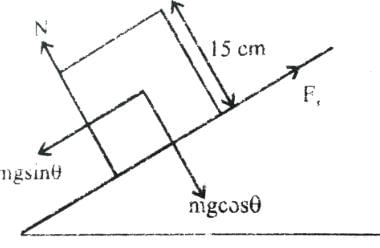
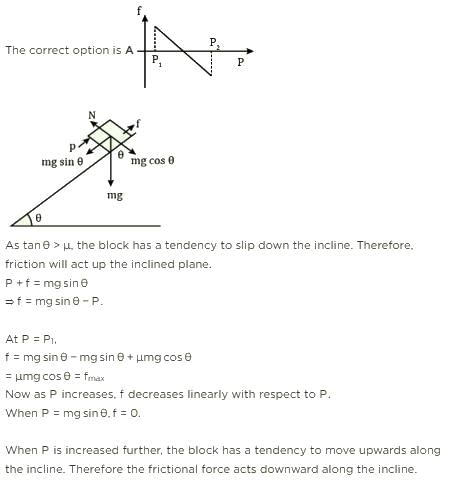
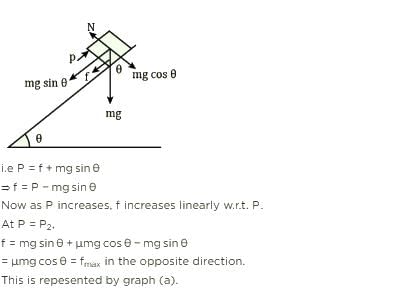
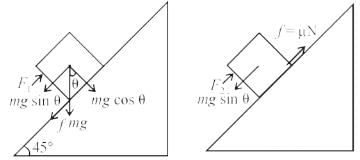
A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle q. The coefficient of friction betwen the block and the plane is m and tan q > m. The block is held stationary by applying a force P parallel to the plane. The direction of force pointing up the plane is taken to the positive. As P is varied from P = mg (sin q _ m cos q ) to Pz = mg (sin q + m cos q), the frictional force f versus P graph will look like [jee 2010]
A block is moving on an inclined plane making an angle 45º with horizontal and the coefficient of friciton is μ. the force required to just push it up the inclined plane is 3 times the force requried to just prevent it from sliding down. If we define N = 10μ, then N is
[jee 2011]
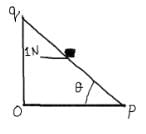
A small block of mass of 0.1 kg lies on a fixed inclined plane PQ which makes an angle with the horizontal. A horizontal force of 1 N acts on the block through its center of mass as shown in the figure. The block remains stationary if (take g = 10 m/s2)