Test: Polity - 4 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Polity - 4
Which of the following statements is correct regarding regulation of citizenship in India?
Consider the following statements:
1. Only Prime Minister can be the Leader of the Lok Sabha and no other Minister can be nominated for it.
2. Vice-President is the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. Only Prime Minister can be the Leader of the Lok Sabha and no other Minister can be nominated for it.
2. Vice-President is the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
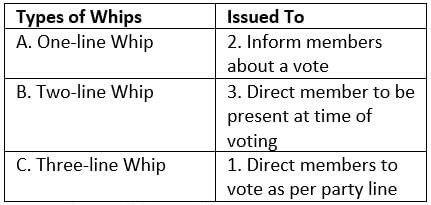
Match the following:
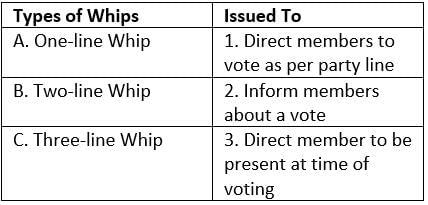
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
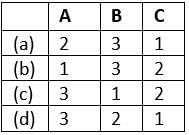

Select the correct answer using the code given below:

Consider the following statements with regard to States and Union Territories:
1. ‘Union of States’ is a wider expression than the ‘Territory of India’.
2. There is division of power between centre and States.
3. The Union Territories and the acquired territories are directly administered by the Central Government.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Which of the following can be considered as accountability checks on Executive?
1. Voting on Demands for Grants.
2. Economy Cut and Token Cut.
3. Close scrutiny by Departmental Standing Committees.
4. Post Budget auditing by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Besides the Fundamental Rights included in Part III, there are certain other rights contained in other parts of the Constitution. In this context, consider the following statements regarding such rights outside Part III of the Constitution:
1. These rights are non-justiciable.
2. These rights are known as constitutional rights or legal rights.
3. Right to Property and Adult Suffrage are example of such rights.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Cultural and Educational Rights mentioned in Indian Constitution:
1. Article 29 recognizes the rights of linguistic minorities only.
2. The educational institutions of minorities do not fall under any regulations of the concerning State authority.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
In context of the power provided by the Constitution to the Union Legislature to reorganize the states, consider the following statements:
1. In case of Union Territory reorganization, reference need to be made to the concerned legislature to ascertain its views.
2. Views of the concerned state legislature/ UT are binding on the President.
3. Such laws does not require a special majority but can be passed by a simple majority.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with reference to the Representation of People Act (RPA), 1951:
1. Section 126A of the RPA deals with the prohibition of conduct of exit poll during the period mentioned therein.
2. Registration of Political parties is governed by the provisions of Section 29A under the RPA, 1951.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements regarding the constitutional provisions for the states in India:
1. The term ‘Union of States’ includes the states mentioned in the First Schedule of the Constitution.
2. A bill contemplating the formation of new states can be introduced in Parliament with the prior permission of President only.
3. The bill needs to be passed by a special majority in both the Houses of the Parliament.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Swachh Shakti event 2019:
1. It aims to highlight the leadership role played by women in Swachh Bharat Mission.
2. Ministry of Jal Shakti organized this event. 3. It was held in Lucknow in Uttar Pradesh.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Who among the following can acquire citizenship by registration in India?
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Lame-Duck session?
1. It is the last session of every existing Lok Sabha.
2. It refers to a session in which members participate for last time because of failure to get re-elected to the new Lok Sabha.
3. This session requires minimum number of members whose presence is essential to transact the business of the House.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
The Gram Nyayalayas Act, 2008 provides for the establishment of Gram Nyayalayas at the grassroots level. In this regard, consider the following statements:
1. Gram Nyayalayas are mobile courts established for every Panchayat at district level.
2. Nyayadhikari are appointed by Chief Justice of the High Court in consultation with the Chief Minister of that state.
3. Gram Nyayalayas have powers of both civil and criminal courts.
4. Gram Nyayalayas are not bound by rules of evidence provided in Indian Evidence Act, 1872.
Which of above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following features express the Principle of Fraternity as mentioned in the Constitution?
1. Dignity of an individual.
2. Integrity of the nation.
3. Unity of the nation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the Contingency Fund of India:
1. According to the Article 267(I) of the Indian constitution, Parliament may by law establish a Contingency Fund of India.
2. Contingency Fund of India shall be placed at the disposal of the Parliament.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
National Data Quality Forum was launched recently, consider the following statements in this regard:
1. It aims to integrate learning from evidence-based initiatives for closing data gap related to population and other health data.
2. It is a multi-stakeholder platform launched by Indian Council of Medical Research and Population Council.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with respect to the term ‘Republic ’mentioned in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
1. In a Republican system the Head of the State is elected.
2. Every democratic country is also a republic.
3. In Presidential form of Government, the Head of the State is indirectly elected while in a Republic, Head of the State is directly elected.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the removal of President:
1. The President can be removed from office, before the expiry of his term, for the “violation of the Constitution”.
2. The impeachment charges against him can be initiated by either House of the Parliament.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
With reference to cabinet committees, consider the following statements:
1. They are established under the Allocation of Business Rules, 1961.
2. Non-cabinet Ministers are not debarred from their membership.
3. They are mostly headed by the Prime Minister.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following is/are the features of Presidential form of government?
1. Separation of Power
2. Wider Representation
3. Unstable government
4. Single Executive
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
1. Free and fair election
2. Efficient implementation of the Right to Information (RTI)
3. Independent Media
4. Establishment of citizen charter in government offices
5. Digitization of records
Which of the above statements will help in bringing transparency in governance in India?
Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
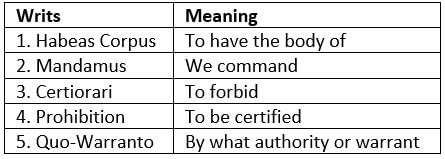
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
1. It is based on the ‘Objectives Resolution’, drafted by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar.
2. It is a part of the Indian Constitution.
3. Since the time of adoption, it has been amended two times.
4. The words Socialist, Secular and Republic were added by 42nd amendment.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the office of Speaker:
1. Speaker is appointed by the President of India.
2. Pro-tem speaker is elected by all the newly elected Members of Parliament from among themselves.
3. Speaker can be removed by the Lok Sabha by a resolution passed by an absolute majority.
Which of the above statements are incorrect?
With reference to Electoral Bonds in India, consider the following statements:
1. These are promissory notes bought by any Indian citizen or company incorporated in India for political party donation.
2. These donations are not tax-deductible.
3. Foreign company registered in India is eligible to make contributions under this scheme.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Which of the following Articles of the Constitution of India says that “the executive power of every State shall be so exercised as not to impede or prejudice the exercise of the executive power of the Union and the executive power of union shall extend to the giving of such directions to a State as may appear to the Government of India to be necessary for that purpose”?
Consider the following statements regarding the disqualification of a member of Parliament on the ground of defection:
1. A member shall be disqualified if he/she gets suspended from the membership of the party on whose ticket he/she was elected.
2. A nominated member shall be disqualified if he/she joins any political party after the expiry of six months.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding freedom to manage religious affairs:
1. According to Article 26, every religious denomination or any of its section has the right to own and acquire movable and immovable property.
2. The rights under Article 26 are subject to public order and morality only.
3. The Supreme Court held that a group must have distinctive name to be designated as a separate religious denomination.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?