Test: Economy NCERT Based Test - 2 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Economy NCERT Based Test - 2
Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary, in its effect?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding the Regular salaried employees:
1. They are paid wages on a regular basis.
2. They are found more in urban areas.
3. They are skilled and qualified.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. They are paid wages on a regular basis.
2. They are found more in urban areas.
3. They are skilled and qualified.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statement:
1) Inflation benefits the debtors
2) Inflation benefits the bond-holders
Which of the statement given above is/are correct?
Read the following statements carefully :
1) GNP = GDP + Net Factor income from abroad
2) NNP = GNP – Depreciation
3) NNP at Factor Cost = NNP at Market Price – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
Which of these statements is correct?
Mahalanobis Model has been associated with which of the following Five Year Plan?
Consider the following factors:
1) Deficit Financing
2) Black Money in an economy
3) High rate of population growth
Which of the factor given below above are responsible for the Demand-pull inflation in an economy?
What do you understand by the disposable personal income?
National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) is an organisation under:
Which one of the following laws stated that the size of the a firm and its growth rate are independent?
Match the following:
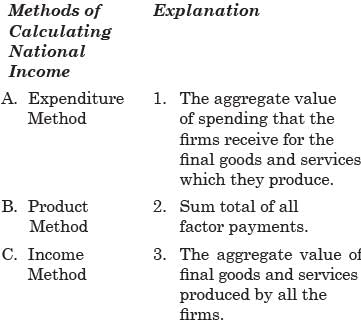
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
What will be the real expression for the measurement of National Income?
Which of the following is correct about the Phillips Curve of an Economy ?
During the planning period in India, the Public Sector was given a leading roll in industrial development. What was/were the objective(s) behind this?
1. Balanced regional growth.
2. To provide goods and services for the welfare of the society, without looking for profi ts.
3. To create more employment opportunities.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following could be the possible ways to overcome the energy crisis in India?
1. Privatization of the power sector.
2. Solar energy should be promoted in tropical countries like India.
3. Reducing transmission and distribution losses.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
With reference to the concept of ‘growth with equity’, consider the following statements:
1. It is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced within the territory.
2. It aims to promote both economic growth and social equality.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements regarding the trade barriers:
1. Tariff barriers refer to the tax imposed on the import of goods by a country to protect domestic goods.
2. Tariff barriers are more explicit in nature than Non-tariff barriers.
3. Tariff barriers are imposed on the quantity and quality of goods, whereas Non-tariff barriers are imposed on the value of goods.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Bretton Woods System re-established a system of Fixed Exchange Rate.
2. Under the Fixed Exchange Rate system, when a government increases the exchange rate making the domestic currency cheaper, it is called devaluation.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Which of the following was/were the reason for the introduction of structural reforms in China after 1949?
1. China was under the compulsion of the International Monetary Fund to introduce economic reforms.
2. The Maoist vision of economic development based on decentralization and self-suffi ciency had failed.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the Worker-Population Ratio:
1. Its proportion is higher in urban areas.
2. Limited availability of resources are the reason for lower workforce participation rates in rural areas.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding power consumption in India:
1. In India, commercial sources of energy contribute the largest share to the total consumed energy.
2. During the post-independence period, the transportation sector was the largest consumer of commercial energy.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements regarding Bilateral Trade:
1. Under bilateral trade, equal trade opportunities are given to both countries involved in the agreement.
2. Under bilateral trade, individual negotiation is necessitated with each country.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Capitalist Economy - Goods are distributed on the basis of the need of the people.
2. Socialist Economy - The government decides how goods are to be produced and how they should be distributed.
3. Mixed Economy - Goods are produced by both public and private entities.
Which of the above pairs is/are incorrectly matched?
Which of the following characterize/s the informal sector credit in India?
1. High-interest rate
2. Debt trap
3. Easy credit access
Select the correct answer using the code given below: