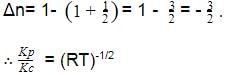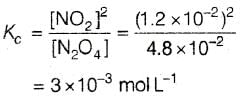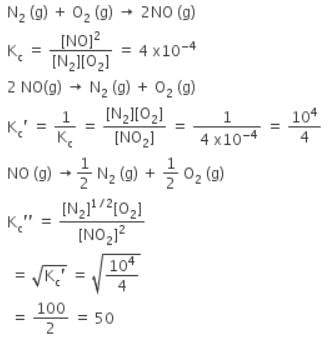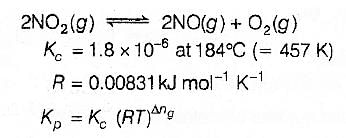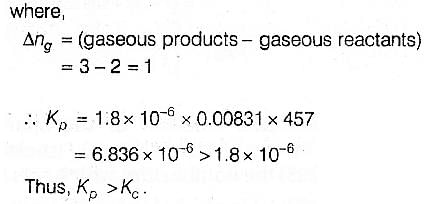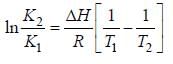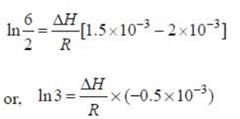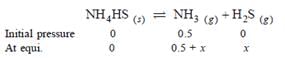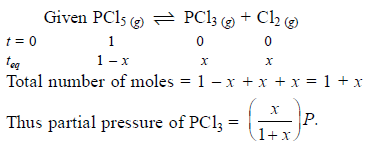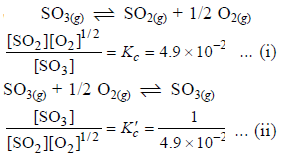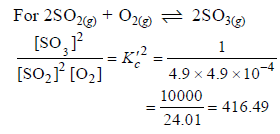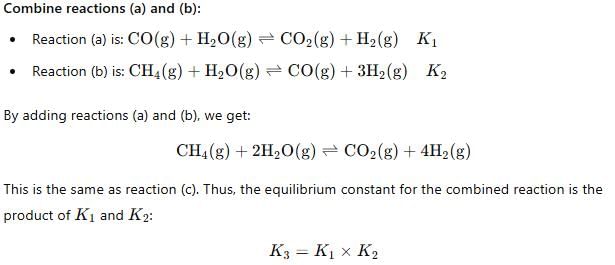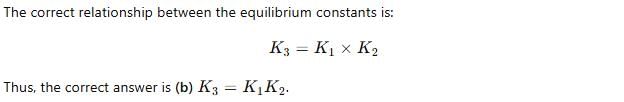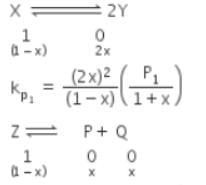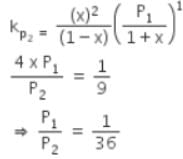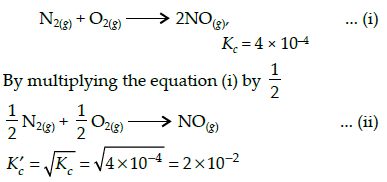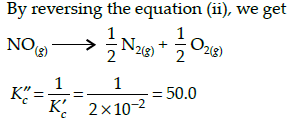Test: Previous Year Questions: Chemical Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Previous Year Questions: Chemical Equilibrium
Which of the following equilibria is not affected by change in volume of the flask
[AIEEE-2002]
For the reaction equilibrium N2O4 (g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g) the concentrations of N2O4 and NO2 at equilibrium are 4.8 × 10-2 and 1.2 × 10-2 mol L-1 respectively. The value of KC for the reaction is -
[AIEEE-2003]
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)⇌2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJ
On the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -
[AIEEE-2003]
What is the equilibrium expression for the reaction P4(S) + 5O2(g) ⇌ P4O10(s) ?
[AIEEE-2004]
For the reaction CO(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ COCl2(g) the KP/KC is equal to -
[AIEEE-2004]
The equilibrium constant for the reaction N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) at temperature T is 4×10-4. The value of KC for the reaction NO(g) ⇌ 1/2 N2(g) + O2(g) at the same temperature is-
[AIEEE-2004]
For the reaction 2 NO2(g) ⇌ 2 NO(g) + O2(g),
(Kc = 1.8 × 10_6 at 184ºC)
(R = 0.0831 kJ/(mol.K))
When Kp and Kc are compared at 184ºC it is found that
[AIEEE-2005]
The exothermic formaton of ClF3 is represented by the equation -
Cl2(g)+3F2(g)⇌ 2ClF3(g) ; ΔrH = -329 kJ
Which of the following will increase the quantity of ClF3 in an equilibrium mixture of Cl2, F2 and ClF3 ?
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
The reaction must be
An amount of solid NH4HS is placed in a flask already containing ammonia gas at a certain temperature and 0.50 atm pressure. Ammonium hydrogen sulphide decomposes to yield NH3 and H2S gases in the flask. When the decomposition reaction reaches equilibrium, the total pressure in the flask rises to 0.84 atm ? The equilibrium constant for NH4HS decomposition at this temperature is
[AIEEE-2005]
Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates as follows, is a closed reaction vessel,
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
If total pressure at equilibrium of the reaction mixture is P and degree of dissociation of PCl5 is x, the partial pressure of PCl3 will be
[AIEEE 2006]
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
SO3(g) ⇌ SO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) is Kc = 4.9×10-2. The value of Kc for the reaction
2SO2(g)+O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) will be
[AIEEE 2006]
For the following three reactions a, b and c, equilibrium constants are given
(a) CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) +H2 (g); K1
(b) CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3H2(g); K2
(c) CH4(g) + 2H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + 4H2(g); K3
Which of the following relations is correct
The equilibrium constants Kp1 and Kp2 for the reactions X ⇌ 2Y and Z ⇌ P + Q, respectively are in the ratio of 1 : 9. If the degree of dissociation of X and Z be equal then the ratio of total pressures at these equilibria is -
[AIEEE 2008]
A vessel at 1000 K contains CO2 with a pressure of 0.5 atm. Some of the CO2 is converted into CO on the addition of graphite. If the total pressure at equilibrium is 0.8 atm, the value of Kp is:
[AIEEE 2011]
The equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction N2(g)+O2(g) → 2NO(g) at temperature T is
4×10-4. The value of Kc for the reaction,
NO(g)→ ½ N2(g) + ½O2(g) at the same temperature is:
[AIEEE 2012]