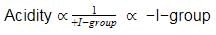Test Level 1: Previous Year Questions - Organic Chemistry - JEE MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - Test Level 1: Previous Year Questions - Organic Chemistry
In the following benzyl/alkyl system R – CH = CH2 or 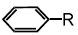 (R is alkyl group) increasing order of inductive effect is –
(R is alkyl group) increasing order of inductive effect is –
[AIEEE-2002]
When 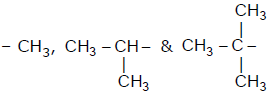 groups are introduced on benzene ring then correct
groups are introduced on benzene ring then correct
order of their inductive effect is -
[AIEEE-2002]
order of their inductive effect is -
The correct order of increasing basic no. of the bases NH3, CH3NH2 and (CH3)2NH is –
[AIEEE-2003]
Rate of the reaction
is fastest when Z is -
[AIEEE-2004]
Consider the acidity of the carboxylic acids :
(a) PhCOOH
(b) o – NO2C6H4COOH
(c) p – NO2C6H4COOH
(d) m – NO2C6H4COOH
Which of the following order is correct ?
[AIEEE-2004]
Which of the following is the strongest base -
[AIEEE-2004]
The decreasing order of nucleophilicity among the nucleophiles
(a)
(b) CH3O-
(c) CN-
(d) 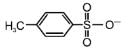
is
[AIEEE-2005]
The reaction
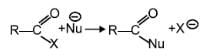
is fastest when X is –
[AIEEE-2005]
Amongst the following the most basic compound is–
[AIEEE-2005]
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to give
CH3Br + Nu- → CH3 – Nu + Br-
The decreasing order of the rate of the above reaction with nucleophiles (Nu-) A to D is
[Nu- = (A) PhO-, (B) AcO-, (C) HO-, (D) CH3O]
[AIEEE 2006]
The correct order of increasing acid strength of the compounds
(a) CH3CO2H
(b) MeOCH2CO2H
(c) CF3CO2H
(d)
is
[AIEEE 2006]
Which one of the following is the strongest base in aqueous solution ?
[AIEEE-2007]
Presence of a nitro group in a benzene ring-
[AIEEE 2007]
Arrange the carbanions,
in order of their decreasing stability-
[AIEEE 2009]
The correct order of increasing basicity of the given conjugate bases (R = CH3) is
[AIEEE 2010]
The strongest acid amongst the following compounds is
[AIEEE 2011]