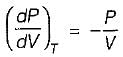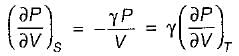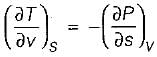Test: Thermodynamic Relations - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermodynamic Relations - 3
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Volume expansivity (β)
B. Joule-kelvin coefficient (μJ)
C. Adiabatic compressibility (KS)
List-ll
1. 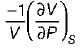
2. 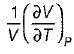
3. 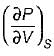
4. 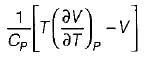
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 4 1
(b) 2 4 1
(c) 3 1 4
(d) 2 1 4
List-I
A. Volume expansivity (β)
B. Joule-kelvin coefficient (μJ)
C. Adiabatic compressibility (KS)
List-ll
1.
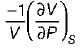
2.
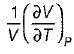
3.
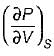
4.
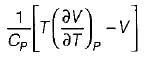
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 4 1
(b) 2 4 1
(c) 3 1 4
(d) 2 1 4
When a real gas undergoes Joule-thomson expansion the temperature
It can be shown that for simple compressible substance, the relationship 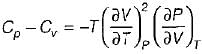 exists where, Cp & Cv are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. T is temperature, Vis volume and Pis pressure. Which one of the following statements is NOT true?
exists where, Cp & Cv are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. T is temperature, Vis volume and Pis pressure. Which one of the following statements is NOT true?
For a given volume of dry saturated steam Clapeyron’s equation is given by
For a single component two-phase mixture the number of independent variable properties are
On a P - V diagram of an ideal gas, suppose a reversible a diabatic line intersects a reversible isothermal line at point A.Then at point A, the slope of the reversible adiabatic line 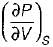 and the slope of the reversible isothermal line
and the slope of the reversible isothermal line 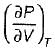 are related as
are related as
Which of the following identities can be most easily used to verify steam table data for superheated steam
For a pure substance, the Maxwell’s reiatior obtained from the fundamental property relation du = Ids - Pdv is


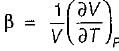
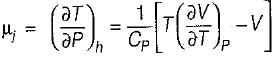
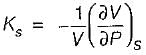
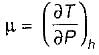

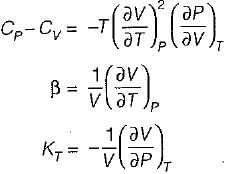
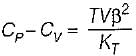
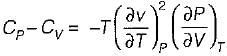
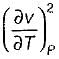 is always positive and
is always positive and 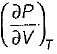 for any substance is negative (Cp - Cv) Is always positive. Therefore Cp is always greater then Cv. When
for any substance is negative (Cp - Cv) Is always positive. Therefore Cp is always greater then Cv. When 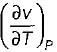 = 0 (for water at 4°C when density is maximum or specific volume minimum), Cp - Cv.
= 0 (for water at 4°C when density is maximum or specific volume minimum), Cp - Cv.