Test: Oogenesis - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Oogenesis
Oogenesis is the process in the ovary that results in the production of female gametes. Which statement about oogenesis in humans is FALSE?
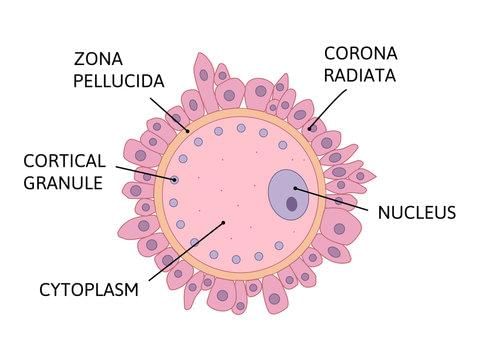
The ovum in the stroma of the mammalian ovary is enclosed in a perforated membrane. It is:
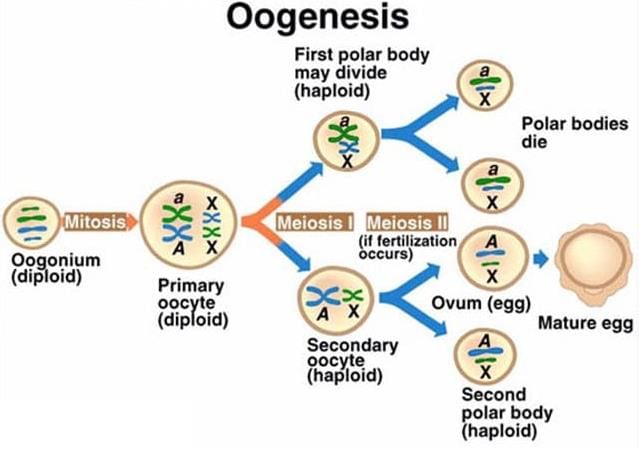
During growth and differentiation of oogenesis, the nucleus of primary oocytes remains in:
What is the stage of the cell cycle at which primary oocytes are arrested?
The female hormone that causes deposition of fat in the breasts and hips, as well as growth of pubic hair, during puberty is:
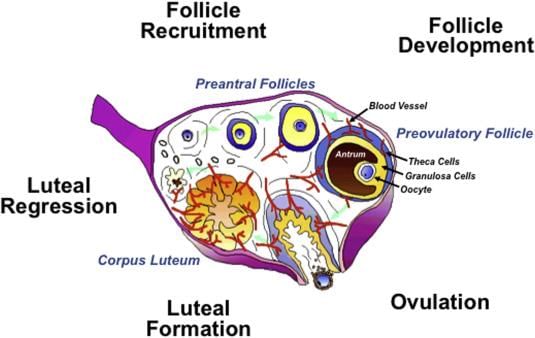
A human female has the maximum number of primary oocytes in her ovaries:
Number of eggs released in the lifetime of a woman is approximately:
Which hormone is responsible for the maturation of ovarian follicles?
Which of the following is the correct set of ploidy and cell type?
Which part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation?